博文
李超,罗晓容等——莺歌海盆地乐东斜坡区乐东A构造储层超压形成机制及其对天然气成藏的启示
||
莺歌海盆地乐东斜坡区乐东A构造储层超压形成机制及其对天然气成藏的启示
李 超1, 2 罗晓容1, 2 范彩伟3 张立宽1, 2
刘爱群3 李 虎3 李 俊4
(1. 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所 北京 100029;2. 中国科学院地球科学研究院 北京 100029;3. 中海石油(中国)有限公司湛江分公司 广东湛江 524057;4. 中国地质大学(武汉)资源学院 武汉 430074)
摘 要 莺歌海盆地乐东斜坡区乐东A构造深层超压天然气资源丰富,查明超压形成机制对于认识乐东斜坡区天然气运移成藏过程和地层压力准确预测至关重要。根据超压测井响应、数值模拟及天然气成藏条件解剖讨论了乐东A构造储层超压成因机制,分析了储层强超压形成与天然气成藏的关系。结果表明:乐东A构造中新统储层普遍发育超压,压力系数最大可达2.27,接近地层破裂压力梯度,纵向上压力系数发生突变。富泥地层快速埋藏导致的机械压实不均衡作用可使压力系数达到1.5~1.6左右。强超压(压力系数>1.6)表现出明显的卸载响应特征,表明储层压力远高于原位泥岩压力。储层中卸载型超压主要是由三亚组超压沿断层垂向传递作用引起的。储层强超压的形成与天然气运移成藏过程密切相关,深层成熟—高成熟的三亚组烃源岩提供了强超压传递的流体来源,烃源岩与储层之间发育的隐伏断裂/微裂隙系统为天然气垂向运移及超压垂向传递提供了有利通道,天然气晚期充注有利于透镜状砂体中传递超压的保存。研究认识将为钻前压力预测和安全钻井设计提供有效参考,并为莺歌海盆地非底辟区高温高压天然气成藏过程提供新的见解。
关键词 超压成因 机械压实不均衡 超压传递 天然气成藏 乐东斜坡区 莺歌海盆地
Generation mechanism of overpressure and its implication for natural gas accumulation in Miocene reservoir in Ledong A structrure, Ledong slope, Yinggehai Basin
Li Chao1,2 Luo Xiaorong1,2 Fan Caiwei3 Zhang Likuan1,2 Liu Aiqun3 Li Hu3 Li Jun4
(1. Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029; 2. Innovation Academy for Earth Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029; 3. Zhanjiang Branch of China National Offshore Oil Corporation Ltd., Zhanjiang, Guangdong 524057; 3. School of Earth Resources, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Wuhan 430074)
Abstract
The Ledong A structure is located in the non-diapir zone of the Ledong slope in the southeast of the Yinggehai Basin with plentiful overpressured natural gas resources. It is important to identify the origin of the overpressure for the understanding of the migration and accumulation process of natural gas, and as well as for the pre-drilling pressure prediction. Based on the overpressure logging responses, numerical modelling and the investigation of natural gas accumulation conditions, the overpressure generation mechanisms in Ledong A structure are discussed, and the relationship between high-magnitude overpressure formation and natural gas accumulation is analyzed. The results show that the overpressure commonly occurred in Miocene reservoirs in the Ledong A structure, with a maximum pressure coefficient of 2.27, which is close to the fracture pressure gradient, and the pressure coefficient abrupt elevated vertically. The disequilibrium compaction caused by the rapid deposition and burial of the mud-dominated layer is the most common cause of overpressure, which can make the pressure coefficient reach about 1.5~1.6. The high-magnitude overpressures (pressure gradient>1.6) in the reservoirs show obviously unloading response, indicating that higher reservoir pressure than the in-situ mudstone pressure. The unloading overpressure is mainly vertically transferred of the deep overpressure via the opening fault. The formation of high-magnitude overpressure in the reservoir is closely related to the process of natural gas migration and accumulation. The overpressured natural gas came from the underlying mature-highly mature Sanya Formation coal-type source rock, and the fluid flow from the source rock vertically through the hidden faults/microfractures to the shallower reservoirs, which caused the vertical transfer of the overpressure. The natural gas charging time is relatively late, so it is conducive to the preservation of the transferred overpressure in the lenticular sandbodies. The results will provide effective guidance for predrilling pressure prediction, and provide a new insight into the migration and accumulation of natural gas in the Yinggehai Basin.
Keywords Overpressure mechanisms, Disequilibrium compaction, Overpressure transference, Natural gas accumulation, Ledong slope, Yinggehai Basin
莺歌海盆地是典型的高温高压富气盆地,中深层(>2 800 m)含气系统中存在高温超压气藏,地温梯度约50℃/km,泥浆密度高达2.30 g/cm3,安全钻井窗口极窄,溢流、井漏等钻井事故频发,阻碍了天然气的勘探开发进程(谢玉洪等,2016)。莺歌海盆地气藏超压引起了诸多学者的关注,目前研究集中于盆地中央底辟带(Xie et al.,2001;王振峰等,2004;金博等,2008;冯冲等,2013)。中新世以来较高的沉积速率导致的泥岩机械压实不均衡是盆地内最普遍的超压成因(Luo et al.,2003;Lei et al.,2011)。底辟区深部流体通过底辟通道或断裂系统发生垂向运移,使深部超压传递至浅部导致浅部渗透性地层发育强超压(Xie et al.,2001;Luo et al.,2003)。与断裂有关超压的产生和存在表明油气成藏动力学条件的改变,不仅能够促进浅部储层内油气成藏,而且影响着油气运移的方向和方式(郝芳等,2003;罗晓容,2004)。
乐东A构造位于莺歌海盆地中央坳陷东南部非底辟区,中深层岩性油气藏是莺歌海盆地重要的勘探领域。乐东A构造峡谷水道和海底扇砂岩中发育高温超压气藏,勘探潜力巨大。储层埋深一般超过4 000 m,地层温度高达220℃,地层压力系数接近2.30,超压与天然气分布关系复杂(谢玉洪,2011;李绪深等,2020)。目前几乎没有详细的研究分析乐东A构造超压成因机制,由于位于乐东斜坡非底辟区,研究人员倾向于将乐东A构造超压成因机制归结为机械压实不均衡与生烃增压(周文等,2014;李文拓等,2020)。然而,平衡深度法和伊顿法却均难以准确超压纵向分布(梁豪等,2020;张祯祥等,2020),不同井同一砂体间地层压力存在明显差异的现象也得不到合理的解释。实际上,乐东A构造超压形成受沉积—埋藏条件、砂体连通性和断裂活动性等因素的共同影响,超压成因及分布复杂,压力预测难度大。因而,对于乐东A构造超压形成机制及其与天然气成藏的关系需要进一步深入研究。
本文基于超压形成地质条件细致解剖,结合超压测井响应及数值模拟,认识乐东斜坡区乐东A构造中新统储层超压主要形成机制,重点讨论强超压形成过程与天然气运移成藏之间的关系,证实断裂传递超压在非底辟区存在的可能性。研究认识将为莺歌海盆地非底辟区超压与天然气形成过程提供新的见解,并以期为钻前压力预测和安全钻井设计提供理论指导。
1 区域地质背景
莺歌海盆地是我国南海北部海域新生代大型走滑伸展盆地,盆地整体呈北西—南东向菱形展布。莺歌海盆地进一步可划分为河内坳陷、莺东斜坡、中央坳陷和莺西斜坡等一级构造单元。受晚期右旋走滑拉分作用控制,中央坳陷形成了多排呈南北向左阶雁列式展布的底辟构造,即中央底辟带(图1a)。自新近纪以来,莺歌海盆地一直处于连续沉积状态,目前沉积物处于最大埋藏深度。乐东斜坡区位于中央坳陷东南部与莺东斜坡之间的过渡带,平均海水深度约为85 m,乐东A构造位于乐东斜坡非底辟区(图1b)。
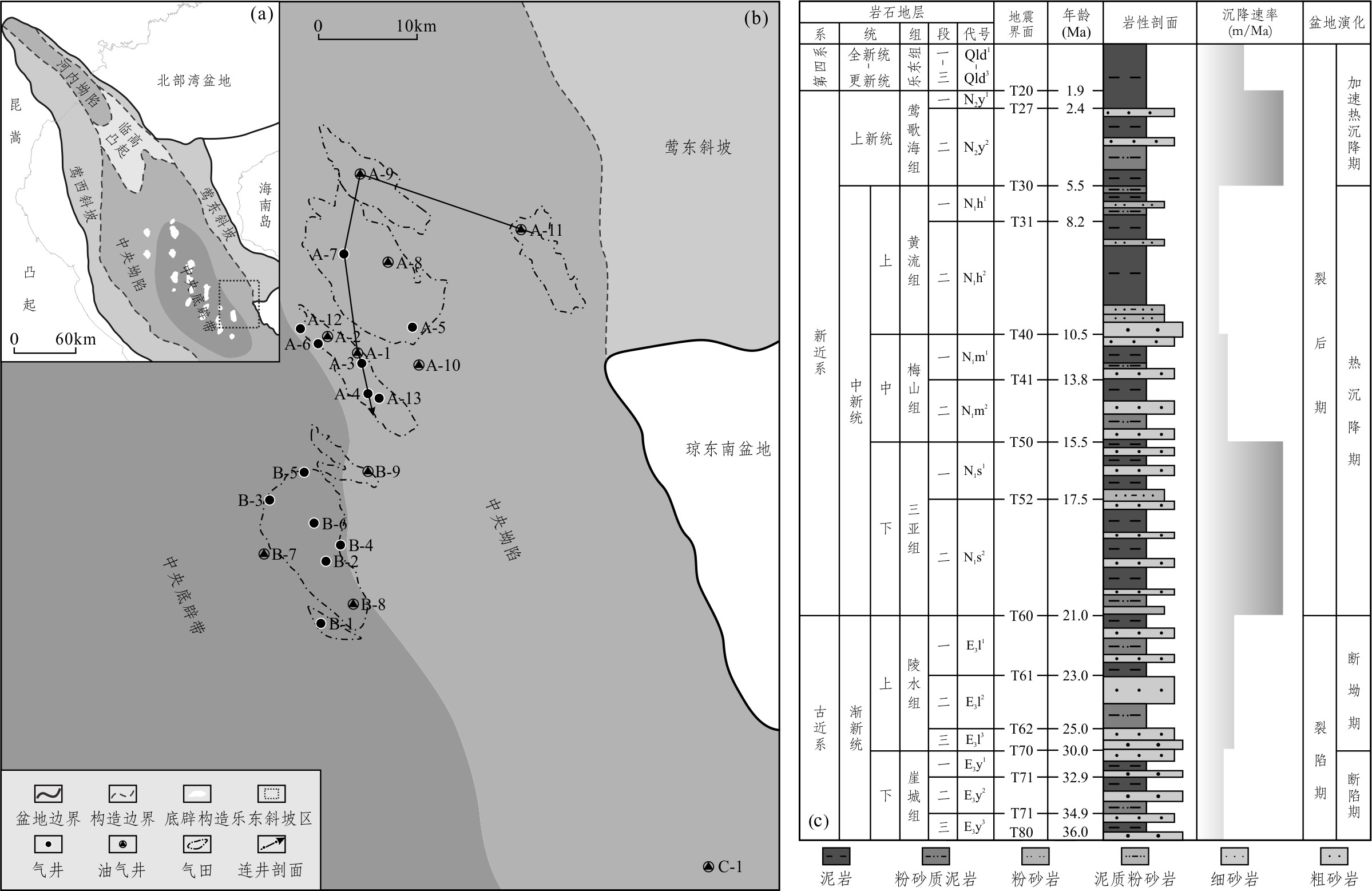
图1 莺歌海盆地构造单元划分、乐东A构造井位分布和地层综合柱状图
Fig. 1 Structural map of Yingghai Basin, the well location of Ledong slope and the generalized
stratigraphic section of the Yinggehai Basin
莺歌海盆地新生代地层自下而上包括渐新统崖城组和陵水组,中新统三亚组、梅山组和黄流组,上新统莺歌海组和第四系乐东组(图1c)。渐新统崖城组和陵水组为浅海和海岸平原相含煤地层,仅在临高凸起及斜坡带被部分钻井揭示。三亚组和梅山组海相泥岩含较丰富腐殖型有机质,是莺歌海盆地的主力烃源岩,黄流组、莺歌海组和乐东组为主要储层发育段。勘探实践中,莺歌海组—乐东组储盖组合称为浅层,埋藏深度小,压力系数介于1.0~1.5。梅山组—黄流组储盖组合为中深层,埋藏深度较大,压力系数一般超过1.8,地温梯度超过45℃/km,属于高温超压区。
乐东A构造在大型鼻状构造上形成千亿方高温超压大型岩性气田(李绪深等,2020)。储层为中新统黄流组重力流水道和海底扇粉细砂岩和中砂岩,孔隙度介于8%~12%,渗透率峰值区间为0.04×10−3 μm2~0.19×10−3 μm2,为低孔—特低渗储层(杨计海等,2019),上覆莺二段大套厚层泥岩构成乐东A构造的区域盖层。
https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-400480-1308652.html
上一篇:黄少英,张玮,李曰俊等——塔里木盆地中部满深1断裂带的多期断裂活动
下一篇:《地质科学》2022年第1期目次