博文
气凝胶集成木材比现有塑料基材料提供更好的隔热性能
 精选
精选
||
气凝胶集成木材比现有塑料基材料提供更好的隔热性能
诸平
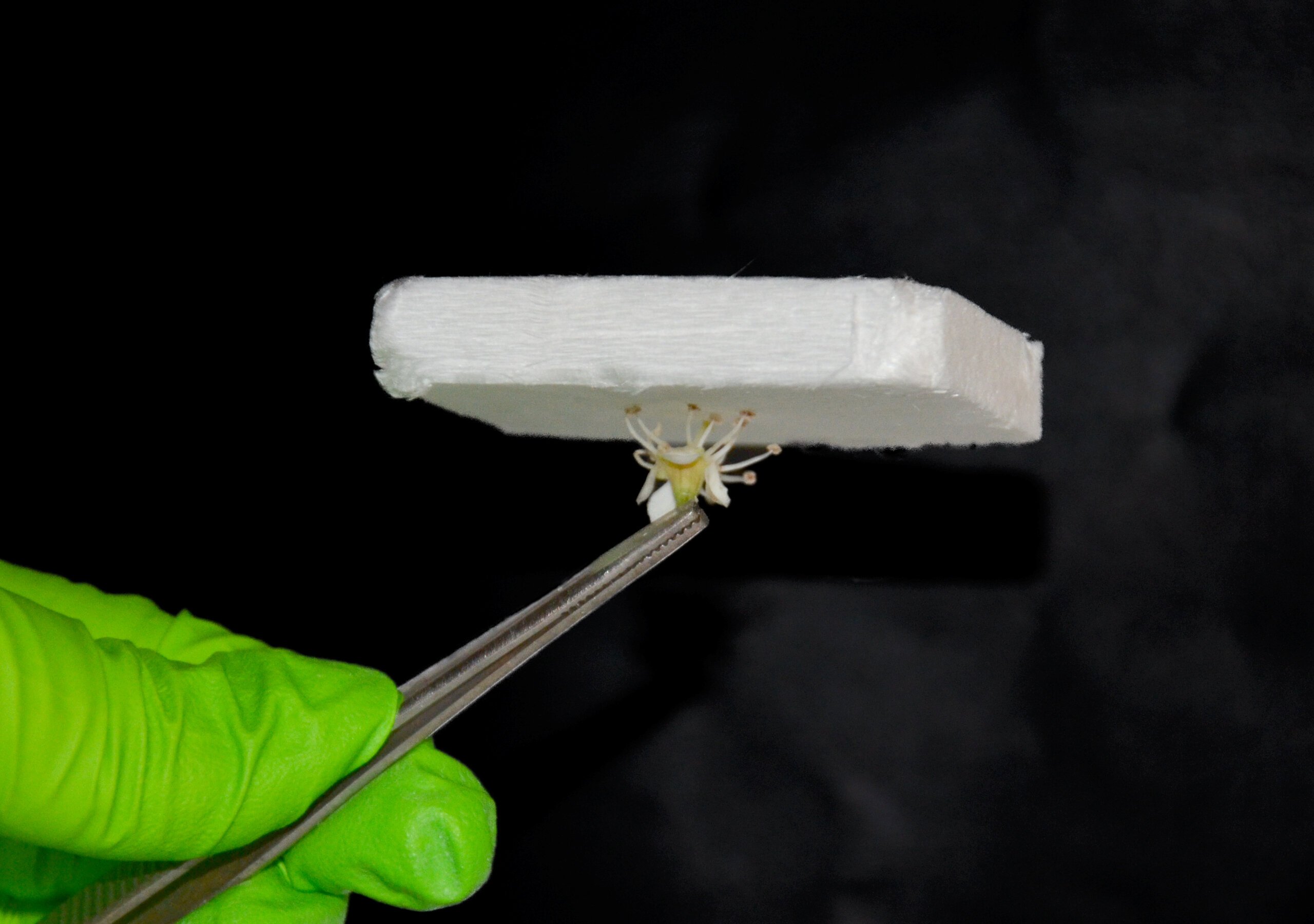


据瑞典皇家理工学院(KTH Royal Institute of Technology)2022年6月7日提供的消息,气凝胶集成木材比现有塑料基材料提供更好的隔热性能(Aerogel integrated wood provides better insulation than existing plastic-based materials)。上述由瑞典皇家理工学院瓦伦堡木材科学中心(Wallenberg Wood Science Center,KTH Royal Institute of Technology)乔纳斯·加雷马克(Jonas Garemark)提供的照片,是由木材纤维素制成的气凝胶隔热材料的特写镜头,它比现有塑料基材料提供更好隔热性能。
不久的一天,通过瑞典研究人员开发的木材绝缘材料,建筑可以变得更加节能和环保。相关研究结果于2022年5月5日已经在《美国化学会应用材料与界面》(ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces)杂志网站发表——Jonas Garemark, Jesus E Perea-Buceta, Daniel Rico Del Cerro, Stephen Hall, Barbara Berke, Ilkka Kilpeläinen, Lars A Berglund, Yuanyuan Li. Nanostructurally Controllable Strong Wood Aerogel toward Efficient Thermal Insulation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(21): 24697–24707. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c04584. Publication Date: May 5, 2022. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.2c04584.研究人员称,新开发的材料具有与普通塑料基绝缘材料一样好甚至更好的隔热性能。
参与此项研究的来自瑞典皇家理工学院的研究人员之外,还有来自芬兰赫尔辛基大学(University of Helsinki, Finland)、瑞典隆德大学( Lund University, Sweden)、瑞典查尔默斯理工大学(Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden)的研究人员。
斯德哥尔摩瑞典皇家理工学院瓦伦堡木材科学中心助理教授李元元(Yuanyuan Li音译)表示,这种新型绝缘材料是一种气凝胶集成木材,不添加任何其他物质。
木材纤维素气凝胶(Wood cellulose aerogels)本身并不是什么新东西。过去几年,研究人员一直在瑞典皇家理工学院瓦伦堡木材科学中心开发先进类型的气凝胶和其他复合材料,但李李元元表示,这种新方法代表着在木材孔隙中控制制备绝缘纳米结构的突破。
“生物基强气凝胶(Biobased strong aerogels)可以用来取代目前的化石基气凝胶(fossil-based aerogels),实现超级隔热(super thermal insulation),有助于能源效率(energy efficiency)、生物经济(bioeconomy)和可持续社会发展(sustainable society development),”李元元说。
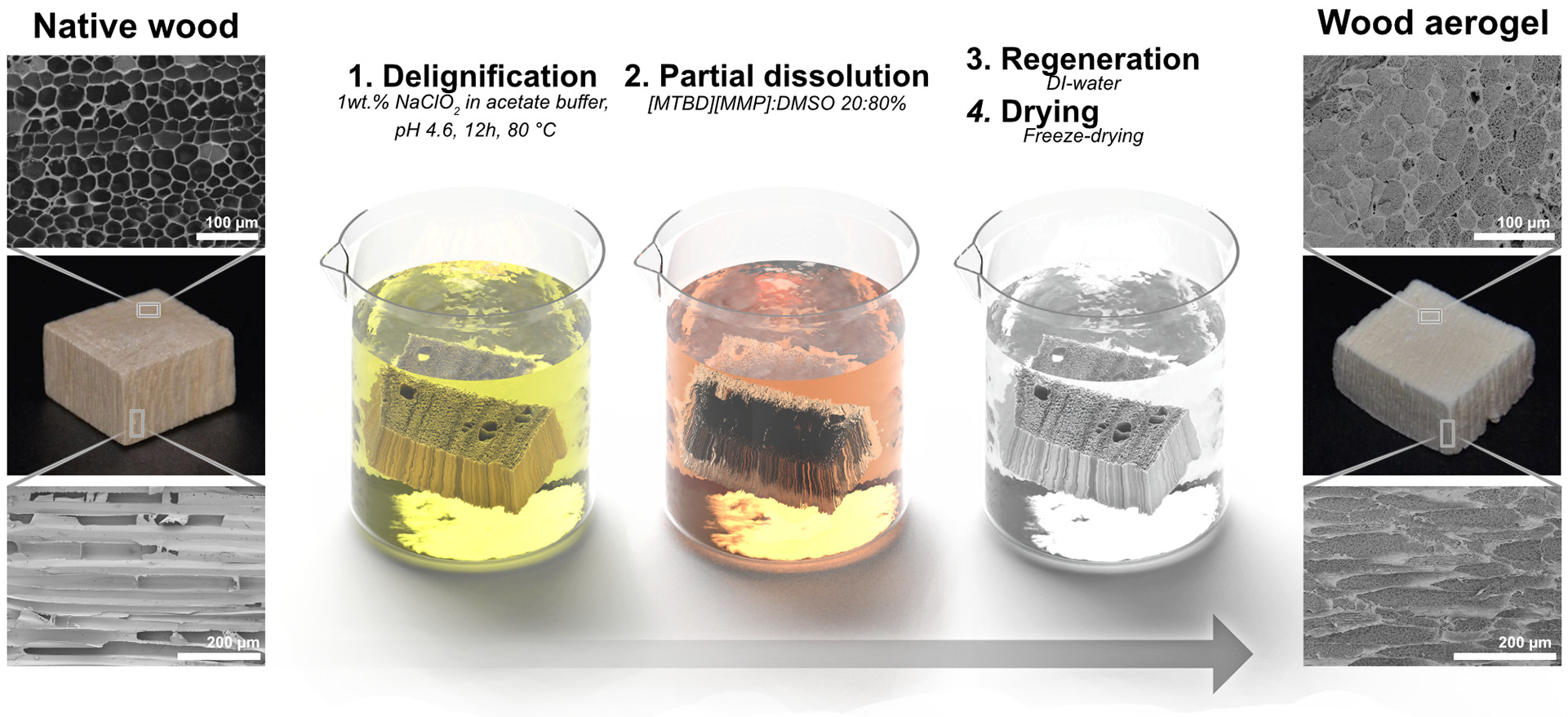
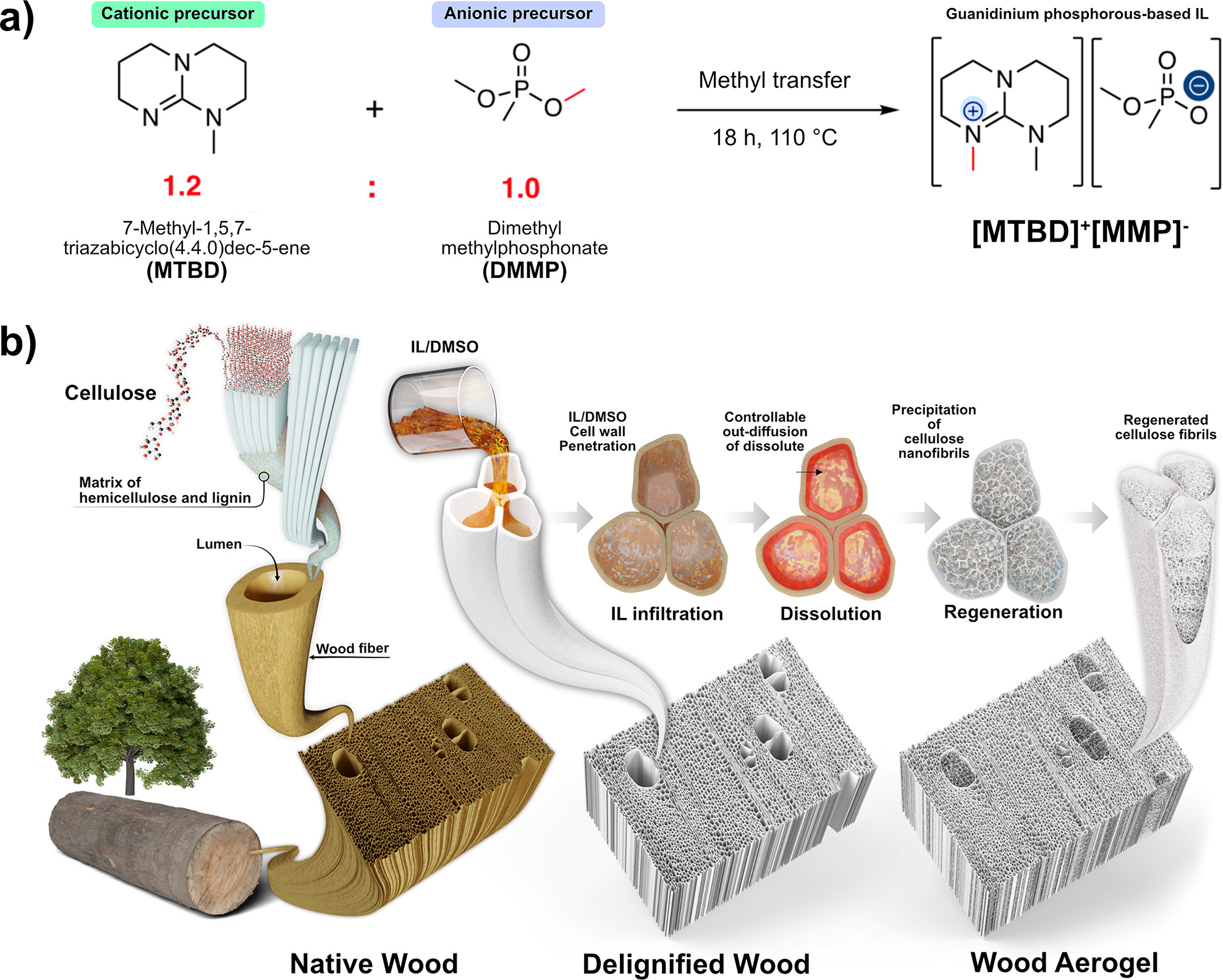
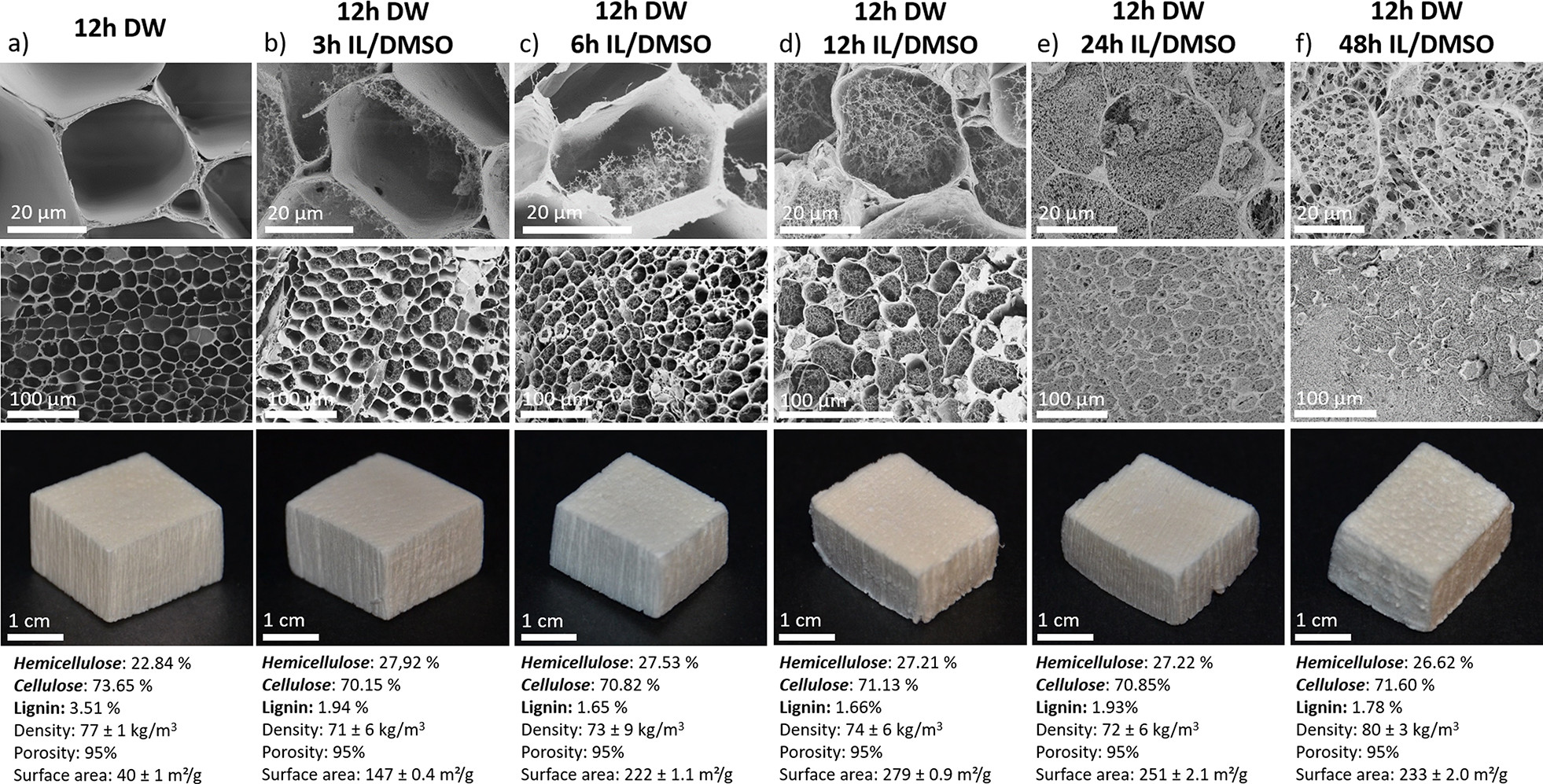
这一过程从木材脱木质素(delignifying)开始,即去除赋予木材颜色和强度的木质素,留下空洞或管腔。降低材料的导热性是通过下一步进入这些大的空孔,并在其中生成更多的纳米孔来实现的,事实上,这些纳米孔有成千上万个。
她说,这些纳米多孔结构是通过细胞壁的部分溶解,然后控制沉淀而形成的。在添加水之前,添加离子液体(ionic liquid简称IL)混合物以部分溶解细胞壁,从而生成纳米纤维网络,使管腔具有纳米多孔性。
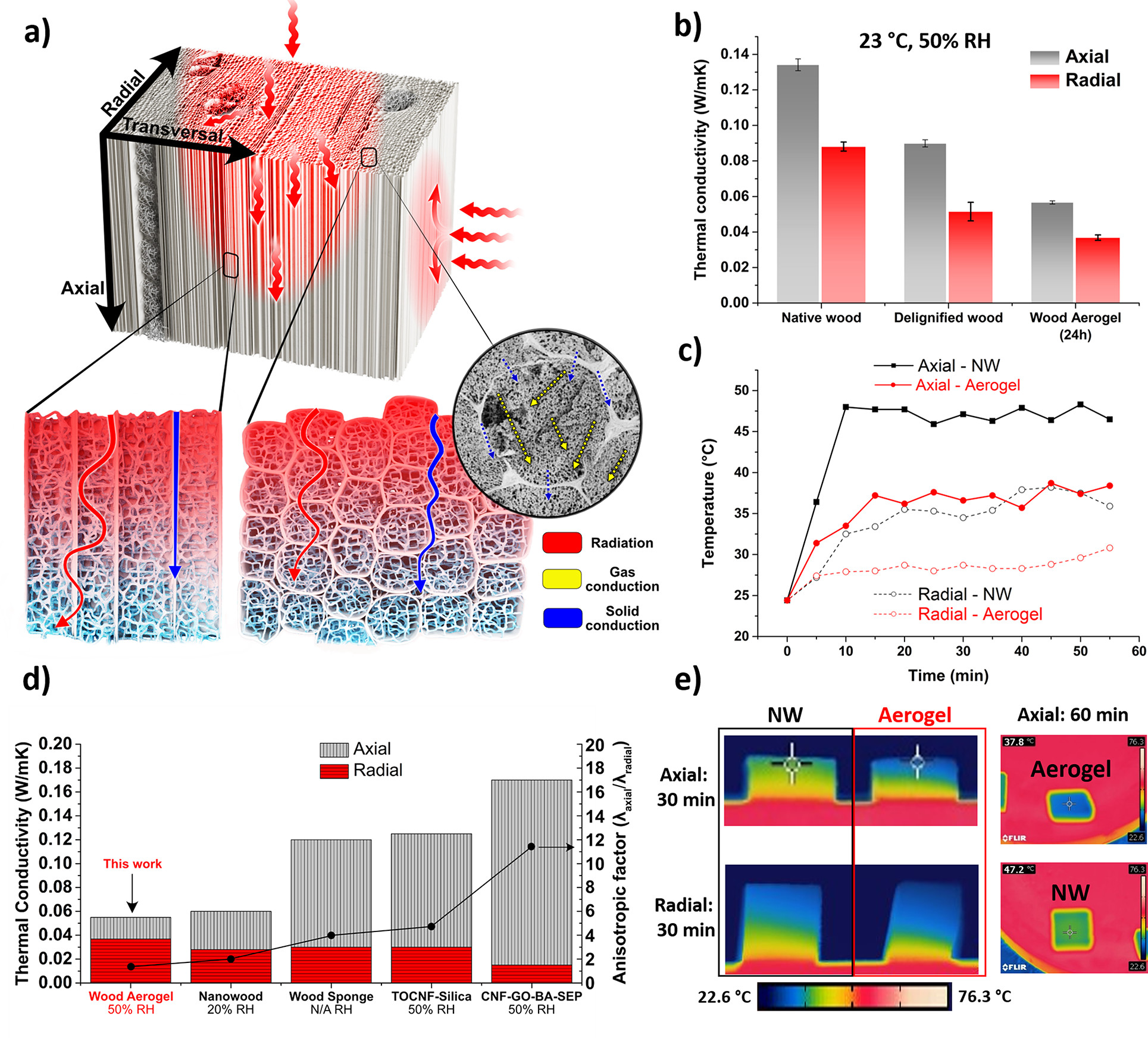
李元元说,研究人员开发了对沉淀过程的高水平控制,这意味着他们可以创建精确水平的纳米孔隙率,以实现理想的导热性(ideal thermal conductivity)。
建筑隔热并非此气凝胶的唯一潜在用途。李元元说,这种独特的结构使先进的材料能够用于能量储存和转换,甚至组织工程。她说:“例如,在包装中,聚苯乙烯(polystyrene)等塑料泡沫有助于防止物体与周围环境之间的热传递,因此可以在运输过程中保持货物凉爽。但在木材的空隙中原位形成纳米纤维网络可以使木材具有高度的隔热性。”
上述介绍,仅供参考。欲了解更多信息,敬请注意浏览原文或者相关报道。
研究团队开发木基泡沫以保持建筑物凉爽(Research team develops wood-based foam to keep buildings cooler)
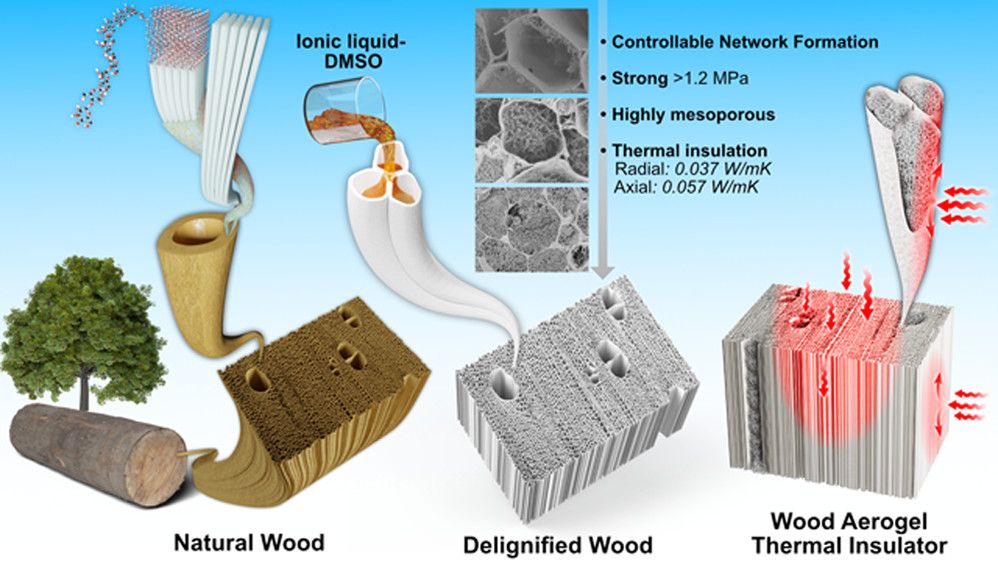
Eco-friendly materials with superior thermal insulation and mechanical properties are desirable for improved energy- and space-efficiency in buildings. Cellulose aerogels with structural anisotropy could fulfill these requirements, but complex processing and high energy demand are challenges for scaling up. Here we propose a scalable, nonadditive, top-down fabrication of strong anisotropic aerogels directly from wood with excellent, near isotropic thermal insulation functions. The aerogel was obtained through cell wall dissolution and controlled precipitation in lumen, using an ionic liquid (IL) mixture comprising DMSO and a guanidinium phosphorus-based IL [MTBD][MMP]. The wood aerogel shows a unique structure with lumen filled with nanofibrils network. In situ formation of a cellulosic nanofibril network in the lumen results in specific surface areas up to 280 m2/g and high yield strengths >1.2 MPa. The highly mesoporous structure (average pore diameter ~20 nm) of freeze-dried wood aerogels leads to low thermal conductivities in both the radial (0.037 W/mK) and axial (0.057 W/mK) directions, showing great potential as scalable thermal insulators. This synthesis route is energy efficient with high nanostructural controllability. The unique nanostructure and rare combination of strength and thermal properties set the material apart from comparable bottom-up aerogels. This nonadditive synthesis approach is believed to contribute significantly toward large-scale design and structure control of biobased aerogels.
https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1342564.html
上一篇:想要降低中风风险?研究人员发现了简单的秘诀
下一篇:能用煤制造石墨吗?看俄亥俄大学的最新研究结果