博文
植物光合作用的自然基因变异
||||
同样是荷兰人的观点评述,同样发表在Trends in Plant Science,作者从多个层面论述了植物光合作用的自然基因变异(Natural genetic variation in plant photosynthesis.pdf)。
A new angle to photosynthesis research
光合作用的基因变异的遗传因子知之甚少
Levels of photosynthetic variation
叶片,植株和冠层都存在光合差异
What is the cause of photosynthetic variation?
这个应该主要由进化决定,当然环境对光合类型的改变有时也很大
Investigations into natural genetic variation in photosynthesis
* Ecophysiological studies
* Agronomic studies
光合基因变异的研究主要集中在生理生态和农艺性状方面
Robust and reproducible phenotyping
重复和积累数据
How to investigate natural genetic variation in photosynthesis
一些生化和分子生物学手段
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
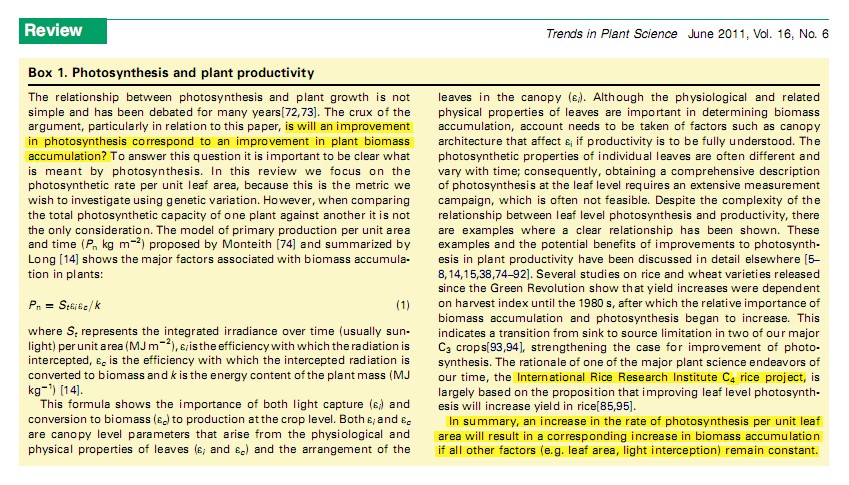
文中光合速率和产量的关系讨论很有意思,一直以来光合作用与作物产量或生物量是大家争论的热点,如光合作用大的,其产量不一定就高。在叶面积和光入射的角度一样的情况,总体而言,光合速率越大的植物往往生物量积累也越多。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
有用的专业词汇表:
Gene
a DNA sequence containing a protein coding region and all the regulatory elements in the direct vicinity needed for transcription of this protein coding region.
a DNA sequence that contributes to the phenotype of an individual, because it comprises a gene or sequences contributing to the expression of a gene.
a quantitative genetic approach used to find genetic associations between genotype and phenotype in a population of individuals of unknown relatedness, to identify genetic loci contributing to such a phenotype.
the specific genetic constitution of an individual, determined by its nuclear and cytoplasmic DNA sequence.
measure of the total leaf area per unit ground area.
the genetic variation that occurs both within (intraspecific) and between (interspecific) species. In this review we focus on spontaneously generated (natural) genetic variation found in crop as well as wild populations, as opposed to variation generated in the laboratory via mutagenesis or transgenesis.
Photosynthesis (oxygenic)
the process by which plants, eukaryotic algae and cyanobacteria use light in the approximate wavelength range of 400–700 nm to split water, forming O2 and reducing CO2 to an organic form, thus converting some of the absorbed light into chemical energy.
the rate of CO2 fixation per unit area of leaf, usually expressed in μmol m–2 s–1; because photosynthesis occurs simultaneously with respiration, the rate of photosynthesis can be qualified as either a gross or a net rate.
the physical appearance of an individual as a consequence of its genotype and its environment.
also known as Amax, this is the maximum photosynthetic rate of a leaf under light saturated conditions; it can also be thought of as the photosynthetic capacity of the plant.
Photosynthetic nitrogen use efficiency
the efficiency with which a plant can use the available nitrogen in its leaves or other photosynthetic tissues for photosynthetic processes.
genetic loci, each corresponding to a region of the genome containing genetic factors for which variation can be found between the studied genotypes, that have a statistically significant association with a particular phenotype, and the trait values of which are expressed in a continuous rather than discrete manner.
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
single base pair variants commonly used as genetic markers in quantitative genetic investigations.
https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-260340-490262.html
上一篇:持续光照对植物生长的影响
下一篇:谷歌13岁了