博文
Plant Biotechnol J:lncRNA在棉花抗真菌病害中的作用
|||
Long noncoding RNAs involve in resistance to Verticillium dahliae, a fungal disease in cotton
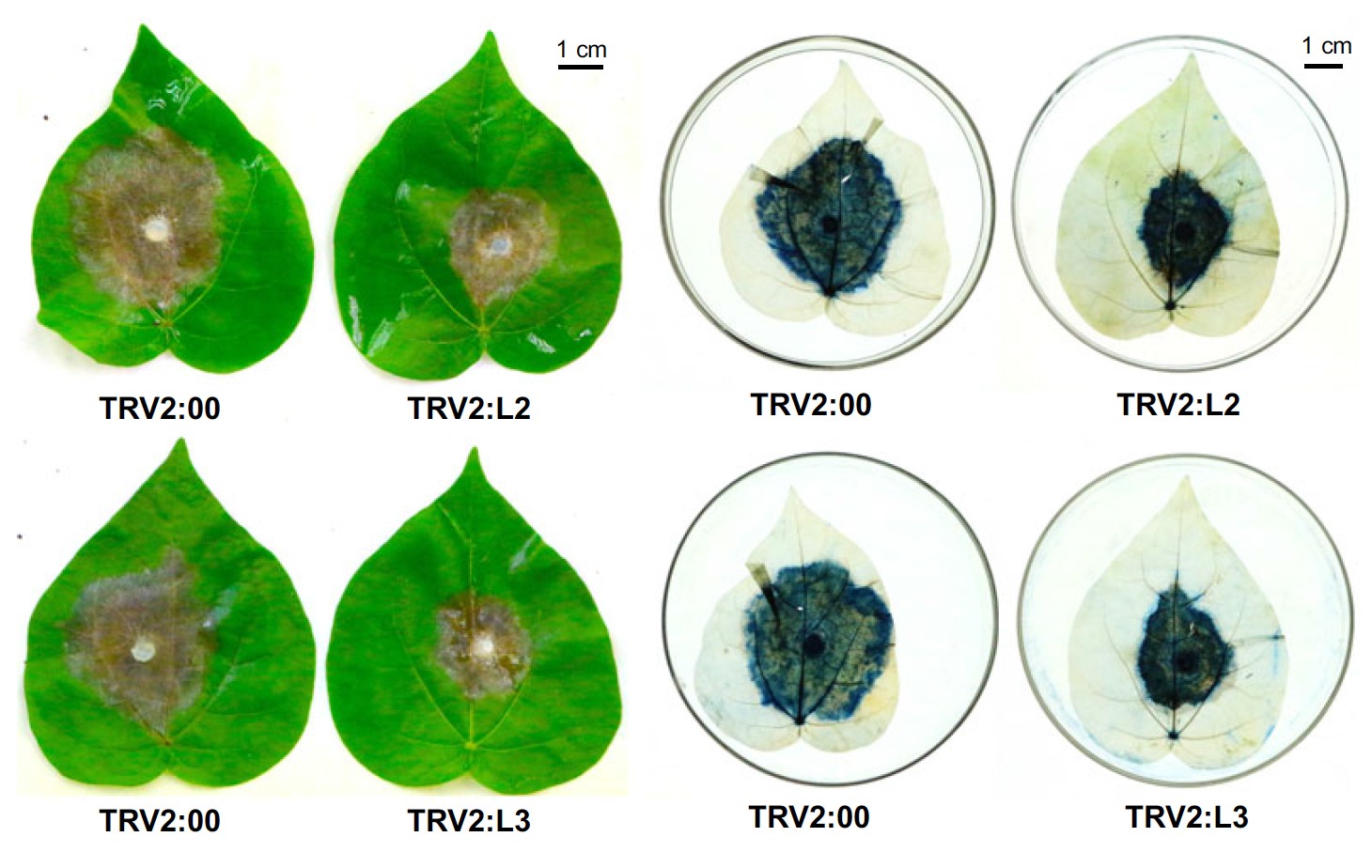
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have several known functions in plant development, but their possible roles in responding to plant disease remain largely unresolved. In this study, we described a comprehensive disease-responding lncRNA profiles in defence against a cotton fungal disease Verticillium dahliae (棉花黄萎病菌). We further revealed the conserved and specific characters of disease-responding process between two cotton species. Conservatively for two cotton species, we found the expression dominance of induced lncRNAs in the Dt subgenome, indicating a biased induction pattern in the co-existing subgenomes of allotetraploid cotton (异源四倍体棉花). Comparative analysis of lncRNA expression and their proposed functions in resistant Gossypium barbadense cv. ‘7124’ (海岛棉) versus susceptible Gossypium hirsutum cv. ‘YZ1’ (陆地棉) revealed their distinct disease response mechanisms. Species-specific (LS) lncRNAs containing more SNPs displayed a fiercer (强烈的) inducing level postinfection than the species-conserved (core) lncRNAs. Gene Ontology enrichment of LS lncRNAs and core lncRNAs indicates distinct roles in the process of biotic stimulus (生物刺激). Further functional analysis showed that two core lncRNAs, GhlncNAT-ANX2- and GhlncNAT-RLP7-silenced seedlings, displayed an enhanced resistance towards V. dahliae and Botrytis cinerea (灰霉病), possibly associated with the increased expression of LOX1 and LOX2. This study represents the first characterization of lncRNAs involved in resistance to fungal disease and provides new clues to elucidate cotton disease response mechanism.
已知长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)在植物发育过程中扮演重要作用,但其在植物抗病响应中的作用还不清楚。本文鉴定了棉花抗真菌病害黄萎病菌过程中疾病响应相关的lncRNA谱。作者进一步揭示了在棉花不同种之间物种保守和特异性两种疾病响应相关lncRNA。对于两个棉花种之间的保守性方面来说,作者发现Dt亚基因组上诱导的lncRNA的优势表达,显示在异源四倍体棉花中存在不同亚基因组偏性的lncRNA诱导模式。lncRNA表达的对比性分析及其在两种棉花(海岛棉和陆地棉)中的抗性分析显示其在不同疾病响应中不同的机制。物种特异性lncRNA含有更多的SNP,要比物种保守性lncRNA在侵染后具有更加强烈的诱导水平。GO富集分析显示物种特异性和保守性lncRNA在生物刺激中表现出不同的作用。进一步的功能分析显示两个保守lncRNA GhlncNAT-ANX2和GhlncNAT-RLP7沉默的植株中都会表现出对棉花黄萎病菌和灰霉病的抗性增强,可能与LOX1和LOX2基因的增强表达相关。本研究是第一个鉴定lncRNA在真菌抗性中的作用,并诠释了棉花疾病抗性新机制。
通讯:张献龙 (http://cotton.hzau.edu.cn/productshow.php?cid=7&id=36)
个人简介:1990年,华中农业大学,博士,方向:农学。
doi: 10.1111/pbi.12861
https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-3158122-1091198.html
上一篇:Nature:森林管理对全球植被生物量的巨大影响
下一篇:Molecular Plant:全基因组复制事件之后基因对间的功能分化
全部作者的其他最新博文
- • Plant Physiology:CsMADS3促进柑果中的叶绿素降解和类胡萝卜素合成(华中农业大学)
- • Molecular Plant:LBD11-ROS反馈调节作用于拟南芥的维管形成层增殖和次生生长(浦项科技大学)
- • Science Advances:根结线虫通过调控植物的CLE3-CLV1模块,促进侵染进程(日本熊本大学)
- • The Plant Cell:拟南芥P小体组分通过对FLC的转录调控,影响开花时间(安徽农业大学)
- • Nature Communications:油菜素内酯参与植物营养生长期转变的分子机制解析(浙江农林大学)
- • Current Biology:光合作用产生的蔗糖驱动侧根“生物钟”(德国弗莱堡大学)