博文
IJMSD | 哥伦比亚大学I.A. Kougioumtzoglou副教授团队:耦合微机械振子阵列的非线性随机动力学
||

图 文 导 读
该文亮点:
1. Buks和Roukes的实验装置被认为是大型静电耦合微/纳振子阵列的一个代表性工作;
2. 考虑随机激励分量的动力学方程的新型建模,表征不同噪声源对系统动力学的影响;
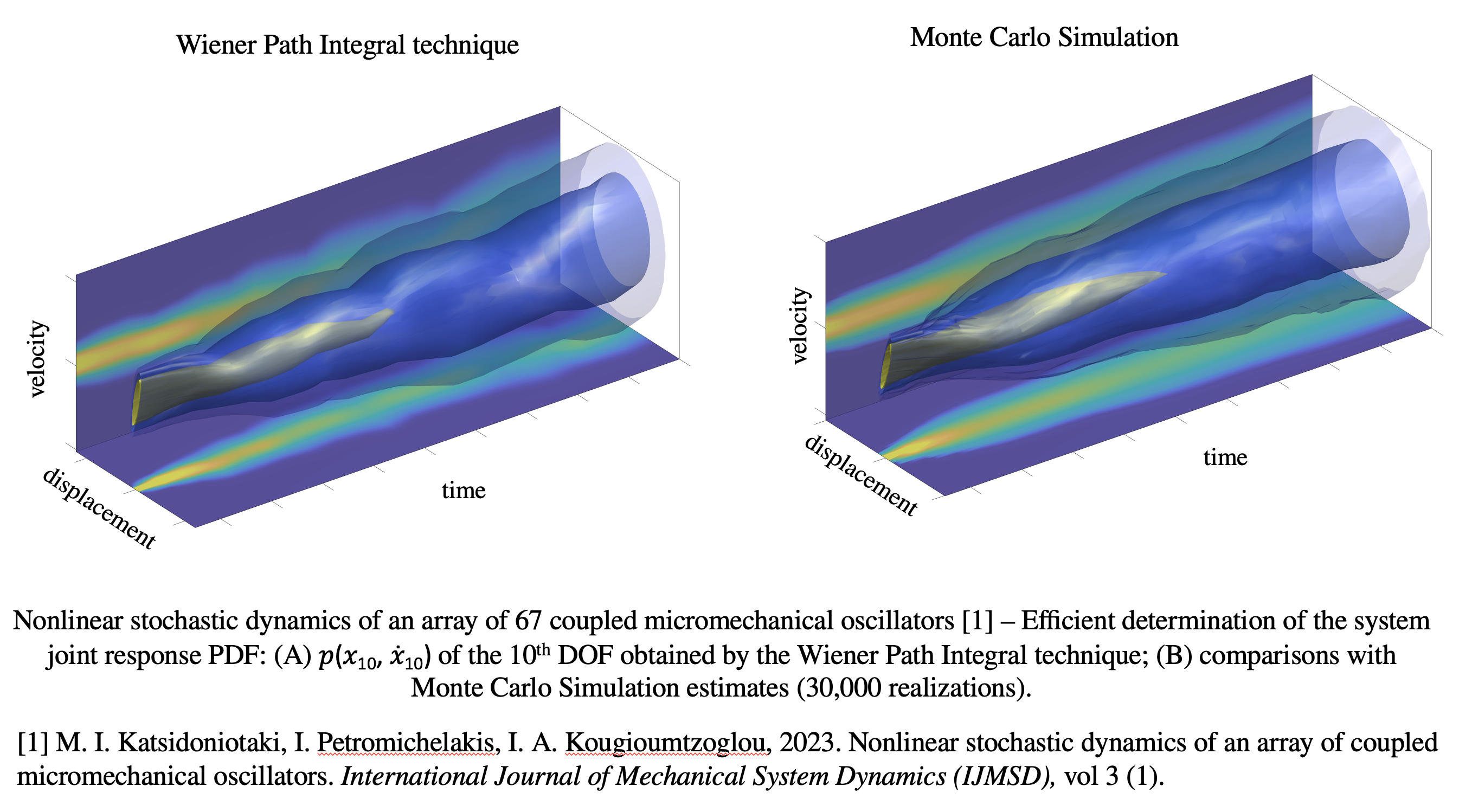
3. 基于维纳路径积分技术进行了准确、高效的随机响应分析。
Highlights:
1. Experimental set-up by Buks and Roukes considered as a representative case of large arrays of electrostatically coupled of micro/nano-resonators.
2. Novel modeling of the equations of motion considering a stochastic excitation component representing the effect of diverse noise sources on the system dynamics.
3. Accurate and computationally efficient stochastic response analysis based on the Wiener path integral technique.
纳米线被视为未来纳米技术中愈发重要的结构构件。近年来,微纳机电器件的发展使快速、可靠、免标记的分子检测成为现实。该技术在当前及未来可被应用于检测与特定疾病有关的生化标志物等,而其检测效率受多种因素影响,如随机性和非线性。这些因素在理解微纳机电器件的检测原理并最终优化纳米机电系统和设备的设计方面起着关键作用。此外,目前的技术能制造出通过电、磁或弹性力耦合的、由数百到数万个微/纳米梁组成的大型阵列。得益于此耦合机制,纳米机电系统的检测灵敏度有望得到增强。
纳米机械系统及设备的优化设计及其检测能力的提升要求:1)建立微/纳振子在随机激励下的非线性多自由度动力学系统模型;2)求解动力学方程并获得系统随机响应需要有效的不确定性传播分析方法。然而,有关非线性微/纳振子的随机建模和分析文献较少,前人研究工作大都与低维(通常为单自由度)系统的解析或数值求解法相关。少数涉及将大型耦合微/纳梁阵列建模为高维多自由度系统的论文采用了大量简化和近似,不可避免地降低了随机响应估计的精确度。
有鉴于此,哥伦比亚大学土木工程与工程力学系Ioannis A. Kougioumtzoglou副教授团队在《国际机械系统动力学学报(英文)》(International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics, IJMSD)发表题为“耦合微机械振子阵列的非线性随机动力学”的研究论文。相较于文献[2-3]中的建模和求解方法,该文创新点如下:1)避免了通常采用的线性或高阶多项式的非线性静电力的近似;2)采用概率建模方法,通过考虑一个随机激励分量来表示不同噪声源对系统动力学的影响;3)精确并低成本求解表征微梁阵列动力学的高维、非线性耦合随机微分方程。文章采用了Kougioumtzoglou副教授及其合作者最新建立的维纳路径积分(Wiener path integral, WPI)高效变分公式。
文献[1]给出的微机械系统的随机响应由WPI技术获得。相较于使用对应30,000次实现的蒙特卡洛仿真,使用WPI技术具有很高的准确性和计算效率。此外,该文提出的模型可在很大程度上捕捉到系统响应的丰富频率成分的显著方面,并且至少可以定性重现Buks和Roukes实验装置的频域响应。
总之,WPI技术精确度高、计算成本低,该独特优势可促进大型微机械振子阵列的随机响应分析达到前所未有的水平;因此,有望引起此类系统及设备优化和设计的范式转变。
Abstract:The stochastic response of a multi-degree-of-freedom nonlinear dynamical system is determined based on the recently developed Wiener path integral (WPI) technique. The system can be construed as a representative model of electrostatically coupled arrays of micromechanical oscillators, and relates to an experiment performed by Buks and Roukes. Compared to alternative modeling and solution treatments in the literature, the paper exhibits the following novelties. First, typically adopted linear, or higher-order polynomial, approximations of the nonlinear electrostatic forces are circumvented. Second, for the first time, stochastic modeling is employed by considering a random excitation component representing the effect of diverse noise sources on the system dynamics. Third, the resulting high-dimensional, nonlinear system of coupled stochastic differential equations governing the dynamics of the micromechanical array is solved based on the WPI technique for determining the response joint probability density function. Comparisons with pertinent Monte Carlo simulation data demonstrate a quite high degree of accuracy and computational efficiency exhibited by the WPI technique. Further, it is shown that the proposed model can capture, at least in a qualitative manner, the salient aspects of the frequency domain response of the associated experimental setup.
Keywords:
Wiener path integral,nonlinear system,stochastic dynamics,nanomechanics
DOI: 10.1002/msd2.12066
Share this article:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/msd2.12066
Cite this article: Katsidoniotaki MI, Petromichelakis I, Kougioumtzoglou IA. Nonlinear stochastic dynamics of an array of coupled micromechanical oscillators. Int J Mech Syst Dyn. 2023; doi:10.1002/msd2.12066
参考文献
[1] Buks E, Roukes L. Electrically tunable collective response in a coupled micromechanical array. Microelectromechanical systems. 2002; 11: 802-807.
[2] Lifshitz R, Cross MC. Response of parametrically driven nonlinear coupled oscillators with application to micromechanical and nanomechanical resonator arrays. Physical Review. 2003; 67: 134302-13.
[3] Zhu J, Ru CQ, Mioduchowski A. High-order subharmonic parametric resonance of multiple nonlinearly coupled microme-chanical nonlinear oscillators. Acta Mechanica. 2010; 212: 69-81.
作 者 简 介

Maria I. Katsidoniotaki Maria I. Katsidoniotaki received her 5-year Diploma in Civil Engineering from the National Technical University of Athens (NTUA) in Greece (2017), and her M.Phil. (2022) and Ph.D. (2023) degrees in Civil Engineering and Engineering Mechanics from Columbia University, New York, USA. Since 2023, she has been working as a Postdoctoral Research Scientist at Columbia University, focusing on stochastic engineering dynamics. Specifically, she develops accurate and computationally efficient stochastic methodologies for uncertainty quantification of complex dynamic systems, including structures and civil infrastructure systems, nanoelectromechanical devices, and physiological mechanisms.
 Ioannis Petromichelakis Ioannis Petromichelakis received his 5-year Diploma in Civil Engineering from the National Technical University of Athens (NTUA) in Greece (2011), his M.Sc. degree from the University of Dresden in Germany (2013), and his Ph.D. degree in Civil Engineering and Engineering Mechanics from Columbia University, New York, USA (2020). His research focuses on path integral techniques and Gröbner basis approaches for stochastic response analysis and optimization of diverse nonlinear dynamic systems, and he has coauthored more than 10 journal papers. He currently works as an Assistant Vice President in Algorithmic Trading at Citibank, USA.
Ioannis Petromichelakis Ioannis Petromichelakis received his 5-year Diploma in Civil Engineering from the National Technical University of Athens (NTUA) in Greece (2011), his M.Sc. degree from the University of Dresden in Germany (2013), and his Ph.D. degree in Civil Engineering and Engineering Mechanics from Columbia University, New York, USA (2020). His research focuses on path integral techniques and Gröbner basis approaches for stochastic response analysis and optimization of diverse nonlinear dynamic systems, and he has coauthored more than 10 journal papers. He currently works as an Assistant Vice President in Algorithmic Trading at Citibank, USA.
 Ioannis A. Kougioumtzoglou Ioannis A. Kougioumtzoglou received his 5-year Diploma in Civil Engineering from the National Technical University of Athens (NTUA) in Greece (2007), and his M.Sc. (2009) and Ph.D. (2011) degrees in Civil Engineering from Rice University, TX, USA. He joined Columbia University in 2014, where he is currently an Associate Professor in the Department of Civil Engineering and Engineering Mechanics. He is the author of approximately 150 publications, including more than 85 technical papers in archival International Journals. Prof. Kougioumtzoglou is a National Science Foundation (NSF) CAREER awardee and a European Association of Structural Dynamics (EASD) Junior Research Prize recipient “for his innovative influence on the field of nonlinear stochastic dynamics.” Prof. Kougioumtzoglou and his research group develop primarily analytic and numerical methodologies for stochastic response analysis, reliability assessment, and optimization of complex engineering systems and structures subject to uncertainties. These methodologies lead eventually to robust and efficient design of dynamic systems ranging from the nano-scale (e.g., nano-mechanical oscillators) to the macro-scale (e.g., energy harvesters and civil infrastructure systems). Specific theoretical research themes include nonlinear stochastic dynamics and path integrals, fractional calculus modeling, computational stochastic mechanics, data-driven uncertainty quantification methodologies, and signal processing techniques.
Ioannis A. Kougioumtzoglou Ioannis A. Kougioumtzoglou received his 5-year Diploma in Civil Engineering from the National Technical University of Athens (NTUA) in Greece (2007), and his M.Sc. (2009) and Ph.D. (2011) degrees in Civil Engineering from Rice University, TX, USA. He joined Columbia University in 2014, where he is currently an Associate Professor in the Department of Civil Engineering and Engineering Mechanics. He is the author of approximately 150 publications, including more than 85 technical papers in archival International Journals. Prof. Kougioumtzoglou is a National Science Foundation (NSF) CAREER awardee and a European Association of Structural Dynamics (EASD) Junior Research Prize recipient “for his innovative influence on the field of nonlinear stochastic dynamics.” Prof. Kougioumtzoglou and his research group develop primarily analytic and numerical methodologies for stochastic response analysis, reliability assessment, and optimization of complex engineering systems and structures subject to uncertainties. These methodologies lead eventually to robust and efficient design of dynamic systems ranging from the nano-scale (e.g., nano-mechanical oscillators) to the macro-scale (e.g., energy harvesters and civil infrastructure systems). Specific theoretical research themes include nonlinear stochastic dynamics and path integrals, fractional calculus modeling, computational stochastic mechanics, data-driven uncertainty quantification methodologies, and signal processing techniques.
欢迎加入读者交流群
长按下图,扫码添加小编微信,邀请您进入IJMSD读者交流群,群内不定期分享期刊论文,并开展学术写作讲座等各项活动。

备注“姓名-单位-IJMSD读者”
期 刊 简 介

IJMSD由来自18个国家的21位院士、17位国际学会主席、20位国际期刊主编等69位科学家和国际出版巨头美国Wiley出版社合作创办。主编为国际机械系统动力学学会(International Society of Mechanical System Dynamics, ISMSD)主席、中国科学院院士、南京理工大学芮筱亭院士,3位合作主编为加拿大工程院院士、欧洲科学院院士、加拿大麦吉尔大学Marco Amabili院士,国际理论与应用力学联盟(International Union of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, IUTAM)前司库、国际多体系统动力学协会(International Association for Multibody System Dynamics, IMSD)前主席、德国斯图加特大学Peter Eberhard教授和美国工程院及科学院院士、欧洲科学院外籍院士、英国皇家学会外籍院士、中国科学院外籍院士、美国工程科学协会前主席、美国西北大学Yonggang Huang院士。
IJMSD旨在用机械系统动力学科学与技术为现代装备设计、制造、试验、评估和使用全生命周期性能的提升提供先进的理论、软件、方法、器件、标准,为全球科学家和工程专家提供广泛的机械系统动力学国际交流平台。IJMSD强调从“系统”视角及系统级工具理解动力学,所涉及的机械系统不仅包括各种不同尺度的机械系统和结构,还包括具有多物理场/多学科特征的综合机械系统。
目前,IJMSD已被ESCI,Scopus,IET Inspec,DOAJ等收录。2023年免收出版费,并为已录用稿件免费提供专业语言润色服务,欢迎全球科学家投稿交流。
期刊主页:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/27671402
投稿网址:
https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/ijmsd
编辑部邮箱:office@ijmsd.net
推 荐 阅 读
IJMSD期刊编辑部版权所有©2023年。任何形式的转载和出版请联系office@ijmsd.net
https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-3296863-1406793.html
上一篇:IJMSD | 东南大学顾宁院士、焦真副教授团队:基于VOF多相流模型的微通道内气-液两相泰勒流传质行为数值模拟
下一篇:IJMSD | 南京航空航天大学金栋平教授团队:基于弹性超材料的空间柔性系绳波动控制
全部作者的其他最新博文
- • IJMSD | 浙江工业大学金江明副教授:构建不对称强非线性结构声系统实现声能量非互易传递
- • IJMSD封面文章 | 青岛大学丁洁玉教授团队:基于多尺度微分代数神经网络的动力系统学习方法
- • IJMSD | 南京航空航天大学裘进浩教授团队:双向能量调节的压电分流阻尼技术及其对结构振动的抑制性能研究
- • IJMSD | 苏州大学凌明祥教授、华南理工大学张宪民教授,等:含曲轴柔性铰链的串并联柔顺机构传递矩阵建模方法
- • IJMSD Themed Collection | Vibration and Control (2022—2023)
- • IJMSD | 中国石油大学(华东)赵德敏副教授团队:温度对双层氮化硼拉伸和振动性能的影响