博文
[转载]CPB封面文章和亮点文章 | 2023年第1期
||
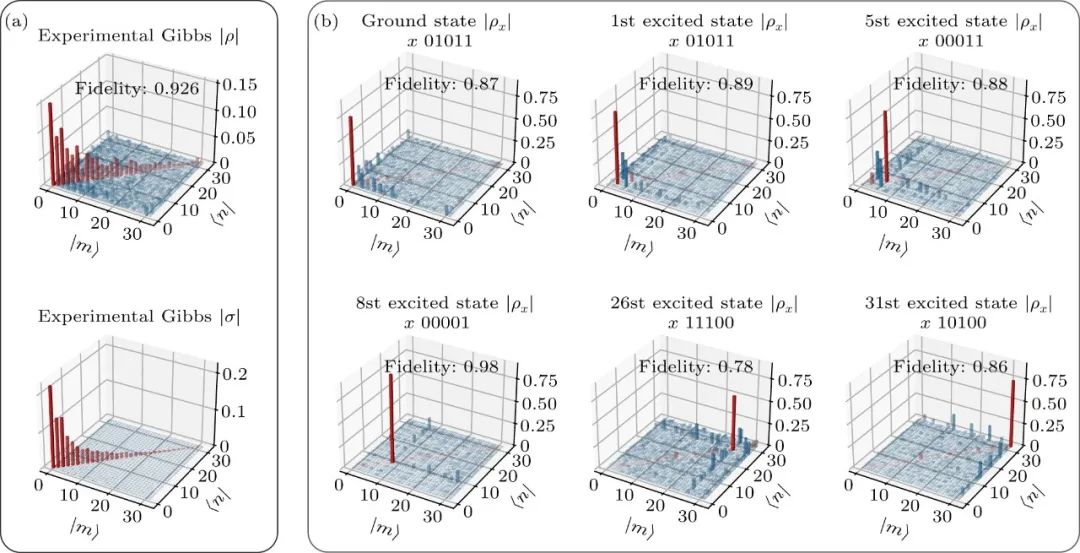
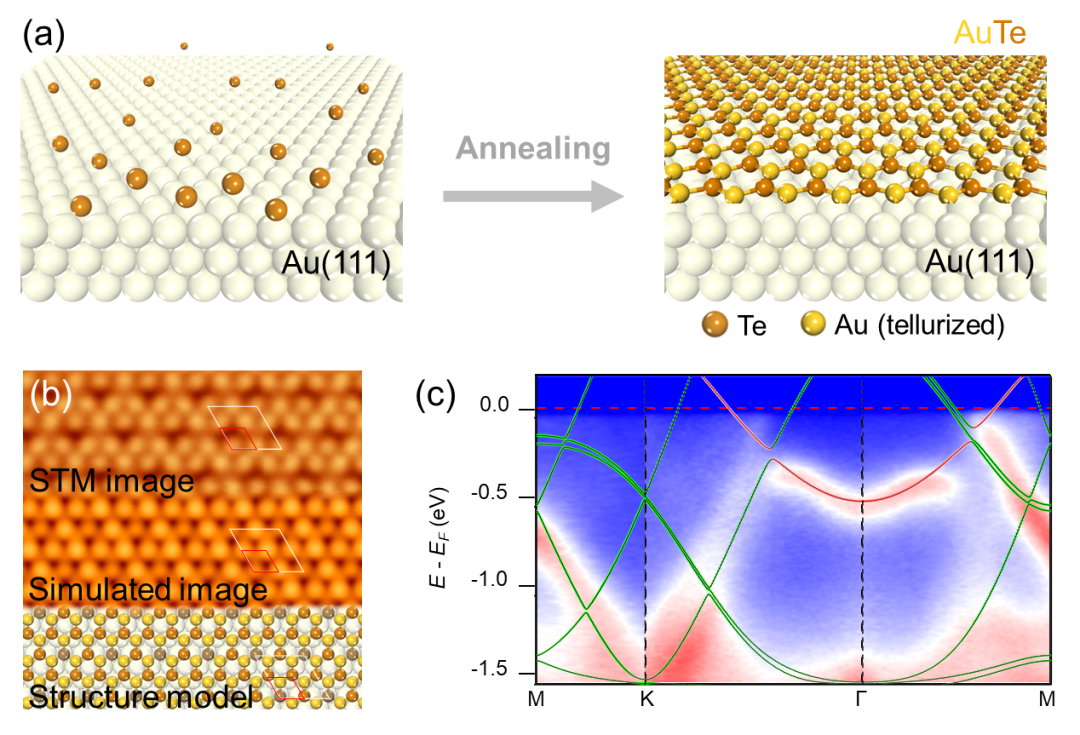
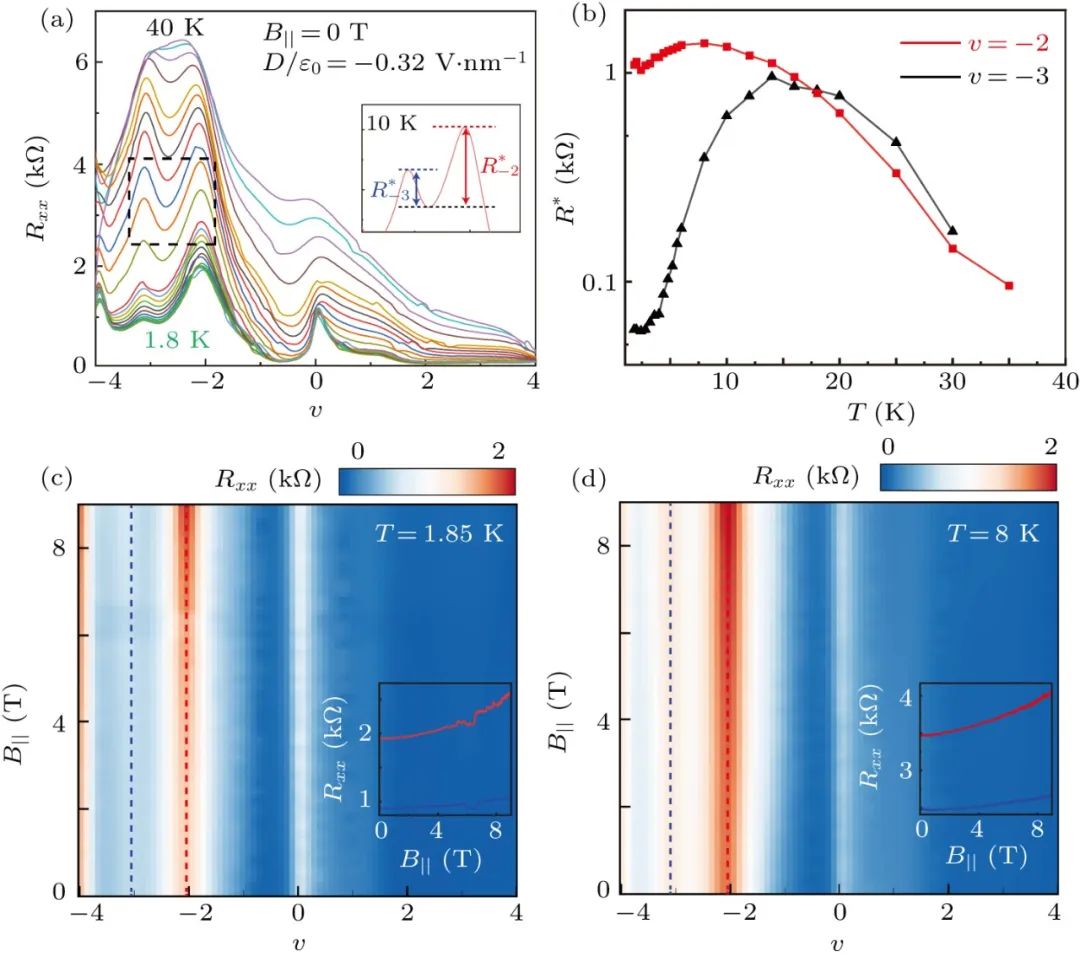
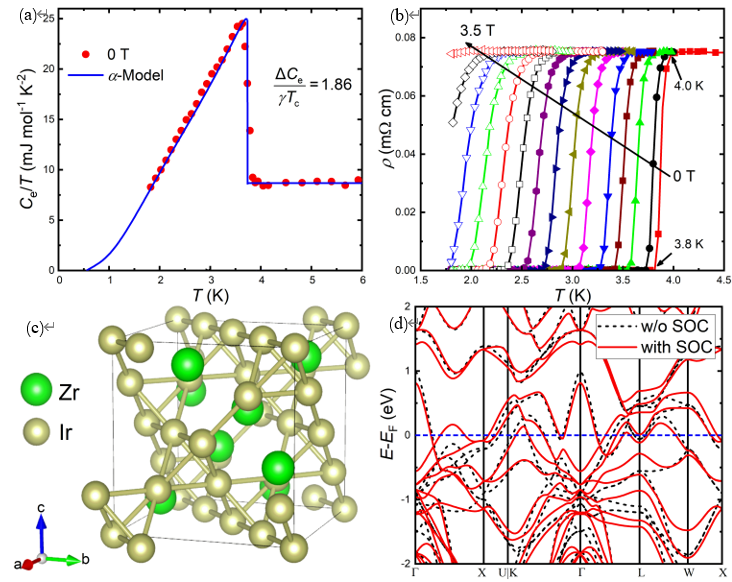
Variational quantum simulation of thermal statistical states on a superconducting quantum processer Xue-Yi Guo(郭学仪), Shang-Shu Li(李尚书), Xiao Xiao(效骁), Zhong-Cheng Xiang(相忠诚), Zi-Yong Ge(葛自勇), He-Kang Li(李贺康), Peng-Tao Song(宋鹏涛), Yi Peng(彭益), Zhan Wang(王战), Kai Xu(许凯), Pan Zhang(张潘), Lei Wang(王磊), Dong-Ning Zheng(郑东宁), and Heng Fan(范桁) Chin. Phys. B, 2023, 32 (1): 010307 量子系统的有限温平衡态对理解凝聚态物理和统计物理中的各种新奇现象具有重要作用。由于多体系统希尔伯特空间维数的指数增长,经典计算机很难做到有效模拟。量子计算技术由于其量子并行性被认为是有效模拟量子多体系统的一种手段,最近,利用变分量子本征求解器(VQE)制备系统基态以及模拟系统的演化有系列进展,但展示量子计算处理有限温平衡态乃至高激发态能力的工作仍比较少,尤其是在含噪声中等规模的(NISQ)量子器件上。 本论文在超导量子处理器上实现了一种经典-量子混合算法来制备量子系统的有限温平衡态。通过将经典机器学习中的生成模型和变分量子算法结合,在实验中制备了5个比特的海森堡XX和XXZ模型的吉布斯态,并展示该方法具有良好的可扩展性和自验证性。同时,实验中还展示了该方法可以制备目标系统的任一激发态,这对在量子计算机上实现对本征态热化假设(ETH)和多体局域化(MBL)的研究具有重要意义。文中也提出一种在量子计算机上计算热力学可观测量的一种减少误差的方法,大大提高了结果的精度和应用性。本论文展示了超导量子计算技术在研究量子热力学问题上的应用前景,对经典-量子混合计算技术的发展具有重要意义。 原文链接 PDF Fig. 1. Density matrices of the Gibbs states and eigenstates obtained in the experiments for XX model. (a) The density matrix of the obtained Gibbs states (upper panel) compared with the exact Gibbs states (lower panel), the fidelity is 92.6%. (b) Density matrix of experimentally prepared eigenstates. In all the plots, only the amplitudes of the density matrix are shown, with diagonal elements and off-diagonal elements colored with red and blue respectively. Fabrication of honeycomb AuTe monolayer with Dirac nodal line fermions Qin Wang(汪琴), Jie Zhang(张杰), Jierui Huang(黄杰瑞), Jinan Shi(时金安), Shuai Zhang(张帅), Hui Guo(郭辉), Li Huang(黄立), Hong Ding(丁洪), Wu Zhou(周武), Yan-Fang Zhang(张艳芳), Xiao Lin(林晓), Shixuan Du(杜世萱), and Hong-Jun Gao(高鸿钧) Chin. Phys. B, 2023, 32 (1): 016102 已有理论预言2D蜂窝状晶格结构的过渡金属单硫族材料极有潜力表现出由镜面保护的狄拉克节线费米子(Dirac nodal line fermions, DNLFs)特征。目前人们通过直接硒化或碲化Cu(111)或Ag(111)单晶已成功实现二维CuSe、AgTe和AgSe等材料的制备及表征,同时理论计算结果表明这三种材料均表现出DNLFs特征。然而,因为样品层与衬底之间具有较强的耦合相互作用,角分辨光电子能谱实验未直接观测到这些材料的DNLFs特征,这使得它们在相关应用的研究上受到很大限制。即使扩展到其他二维体系,实验上也仅限于在单层Cu2Si(具有蜂窝Cu晶格和三角形Si晶格)和三原子层的砖墙型结构的Bi(110)中观测到二维DNLFs。因此,寻找和制备与衬底之间具有弱相互作用的新型二维狄拉克节线材料对于未来应用研究具有重要意义。 本文通过分子束外延技术,以干净的Au(111)单晶为衬底,通过直接碲化的方式成功制备了二维AuTe材料。结合第一性原理计算、低能电子衍射、扫描隧道显微镜以及扫描透射电子显微镜等表征手段,发现样品为生长在(3×3)Au(111)衬底上的具有蜂窝状晶体结构及单原子层厚度的(2×2)AuTe。后续角分辨光电子能谱对样品电子态的表征结果显示,二维AuTe中存在由镜面反演对称性保护的带隙节线环,与理论计算结果一致。值得注意的是,这是实验上首次在过渡金属单硫族材料家族中观测到gapped-DNLFs。与此前报道的CuSe、AgSe和AgTe等过渡金属单硫族材料相比,单层AuTe材料的DNLFs特征更加靠近费米面,这使其有望应用于未来纳米电子器件中。 原文链接 PDF Fig. Schematic of the fabrication, Topography, Geometric and electronic structures of monolayer AuTe on Au(111) surface. (a) Schematic of the fabrication of monolayer AuTe by direct tellurization of the Au(111) substrate. Au atoms in the Au(111) substrate and tellurized Au atoms are shown in light and golden yellow, respectively. (b) Atomic resolution STM image, simulated STM image, and the structure model of monolayer AuTe on Au(111) surface. The red and white rhombi present the AuTe unit cell and ((2×2) superlattice. (c) ARPES data obtained from the monolayer AuTe on Au(111) surface, superimposed with calculated band structure of AuTe. The green and red curves illustrate contributions from in-plane and out-of-plane orbitals. Correlated states in alternating twisted bilayer-monolayer-monolayer graphene heterostructure Ruirui Niu(牛锐锐), Xiangyan Han(韩香岩), Zhuangzhuang Qu(曲壮壮), Zhiyu Wang(王知雨), Zhuoxian Li(李卓贤), Qianling Liu(刘倩伶), Chunrui Han(韩春蕊), and Jianming Lu(路建明) Chin. Phys. B, 2023, 32 (1): 017202 转角范德瓦尔斯异质结为人工构造、原位调控电子关联体系提供了良好的实验平台,涌现出关联绝缘态、磁性、超导、量子反常霍尔效应等诸多新奇物性,引起了广泛的关注和研究兴趣。本文对最经典的转角双层石墨烯进行拓展,进一步转角堆叠双层石墨烯,构成“双层-单层-单层”转角体系,发现在1.74°的较大转角时依然存在关联绝缘峰。不同于转角双层石墨烯,此非对称体系的物性可由电位移场的大小和方向调节。同时,我们在摩尔超晶胞导带和价带分别填充一个电子时,发现了反直觉的熵驱动波梅兰丘克效应:温度升高,电子运动反而冻结。 多层转角样品中关联绝缘态在大转角情况下的坚韧性,以及在空穴摩尔超晶格平带中只填充一个电子(即三个空穴)时首次发现波梅兰丘克效应,表明多层转角体系还有很多新奇物性尚未开发。我们的实验结果为将来灵活设计并深入研究更多种类转角异质结提供了新的思路。 原文链接 PDF Fig. 4. Signature of Pomeranchuk effect at v = –3 (D/ε0 = 0.32 V⋅nm−1). (a) Temperature dependence of resistive peaks at v = –2 and –3. Inset: Definition of the effective magnitudes of correlated peaks with background removed. (b) Non-monotonic temperature dependence of correlated peaks at v = –3 (c). An in-plane magnetic field enhances resistive peaks at v = –2 and –3. (d) The field enhancement is stronger at higher temperature of 8 K. Superconducting properties of the C15-type Laves phase ZrIr2 with an Ir-based kagome lattice Qing-Song Yang(杨清松), Bin-Bin Ruan(阮彬彬), Meng-Hu Zhou(周孟虎), Ya-Dong Gu(谷亚东), Ming-Wei Ma(马明伟), Gen-Fu Chen(陈根富), and Zhi-An Ren(任治安) Chin. Phys. B, 2023, 32 (1): 017402 5d过渡金属铱基化合物具有强自旋轨道耦合(SOC)效应和一系列新颖的物理性质,特别是其铱氧化物同构于高温铜氧化物超导体而受到广泛关注。近来,铱基C15型Laves相AIr2 (A = Ca, Sr, Ba, Th)因其超导电性和强自旋轨道耦合(SOC)效应的共存也引起了人们的研究兴趣。然而,以上AIr2相在空气中极不稳定,限制了该体系的研究。而ZrIr2同样具有C15型晶格结构,其是否具有体超导性仍未被证实,并且超导性质也一直未有详细报道。考虑到ZrIr2在空气中具有良好的稳定性,我们对该化合物的制备、电热输运及其超导电性进行了详细研究。 本文结合实验测量和第一性原理计算,系统研究了Laves相超导体ZrIr2的超导性质。低温电阻率和磁化率表征表明ZrIr2为第二类超导体,其超导转变温度为4.0 K,估算得到的下临界场和上临界场分别为12.8 mT和4.78 T。此外,首次通过比热测量证实了其体超导的性质,超导相变较大的电子比热跃变显示出强的电子-声子耦合。第一性原理计算则表明ZrIr2具有结构简单的三维费米面,并且SOC效应对ZrIr2的能带结构有着显著影响。作为空气中稳定的化合物,ZrIr2为研究C15型铱基超导体中超导电性与强SOC效应之间的相互作用提供了良好的平台。 原文链接 PDF Fig. (a) The electronic contribution of specific heat below 6 K. The solid line shows the fit with α-model. (b) The superconducting transition region on ρ(T) under various magnetic fields up to 3.5 T. (c) The conventional unit cell of ZrIr2. (d) Calculated electronic band structure of ZrIr2 without and with SOC near the Fermi level. TOPICAL REVIEW — Celebrating 30 Years of Chinese Physics B TOPICAL REVIEW — Physics in micro-LED and quantum dots devices TOPICAL REVIEW — The third carbon: Carbyne with one-dimensional sp-carbon SPECIAL TOPIC — Fabrication and manipulation of the second-generation quantum systems SPECIAL TOPIC — Celebrating the 70th Anniversary of the Physics of Jilin University TOPICAL REVIEW—Laser and plasma assisted synthesis of advanced nanomaterials in liquids TOPICAL REVIEW — Progress in thermoelectric materials and devices SPECIAL TOPIC — Emerging photovoltaic materials and devices SPECIAL TOPIC — Organic and hybrid thermoelectrics SPECIAL TOPIC — Superconductivity in vanadium-based kagome materials SPECIAL TOPIC— Interdisciplinary physics: Complex network dynamics and emerging technologies SPECIAL TOPIC — Non-Hermitian physics SPECIAL TOPIC — Unconventional superconductivity SPECIAL TOPIC — Two-dimensional magnetic materials and devices SPECIAL TOPIC — Ion beam modification of materials and applications SPECIAL TOPIC — Quantum computation and quantum simulation SPECIAL TOPIC —Twistronics SPECIAL TOPIC — Machine learning in condensed matter physics SPECIAL TOPIC — Phononics and phonon engineering SPECIAL TOPIC — Water at molecular level SPECIAL TOPIC — Optical field manipulation SPECIAL TOPIC — Modeling and simulations for the structures and functions of proteins and nucleic acids SPECIAL TOPIC —Terahertz physics SPECIAL TOPIC — Ultracold atom and its application in precision measurement SPECIAL TOPIC — Topological 2D materials SPECIAL TOPIC — Active matters physics SPECIAL TOPIC — Physics in neuromorphic devices SPECIAL TOPIC — Advanced calculation & characterization of energy storage materials & devices at multiple scale TOPICAL REVIEW — Advanced calculation & characterization of energy storage materials & devices at multiple scale TOPICAL REVIEW — Quantum dot displays TOPICAL REVIEW — CALYPSO structure prediction methodology and its applications to materials discovery SPECIAL TOPIC — A celebration of the 100th birthday of Kun Huang TOPICAL REVIEW — A celebration of the 100th birthday of Kun Huang SPECIAL TOPIC — Strong-field atomic and molecular physics TOPICAL REVIEW — Strong-field atomic and molecular physics TOPICAL REVIEW — Topological semimetals SPECIAL TOPIC — Topological semimetals SPECIAL TOPIC — Photodetector: Materials, physics, and applications TOPICAL REVIEW — Photodetector: Materials, physics, and applications TOPICAL REVIEW — Fundamental research under high magnetic fields Virtual Special Topic — High temperature superconductivity Virtual Special Topic — Magnetism and Magnetic Materials









https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-3377544-1376525.html
上一篇:[转载]兔年大吉!
下一篇:[转载]CPB2023年第1期编辑推荐文章