博文
EXPRESS LETTER | Valence Quark Ratio in the Proton
|

Received 19 March 2022;
online 24 March 2022
EXPRESS LETTER
Valence Quark Ratio in the Proton
Zhu-Fang Cui (崔著钫), Fei Gao (高飞), Daniele Binosi, Lei Chang (常雷), Craig D. Roberts, and Sebastian M. Schmidt
Chin. Phys. Lett. 2022, 39 (4): 041401
HIGHLIGHT
Using new data, this study delivers the first model-independent prediction for the proton valence-quark ratio: dV/uV(xB→1)=0.230(57), thereby establishing a benchmark against which all pictures of the proton can be measured in future.
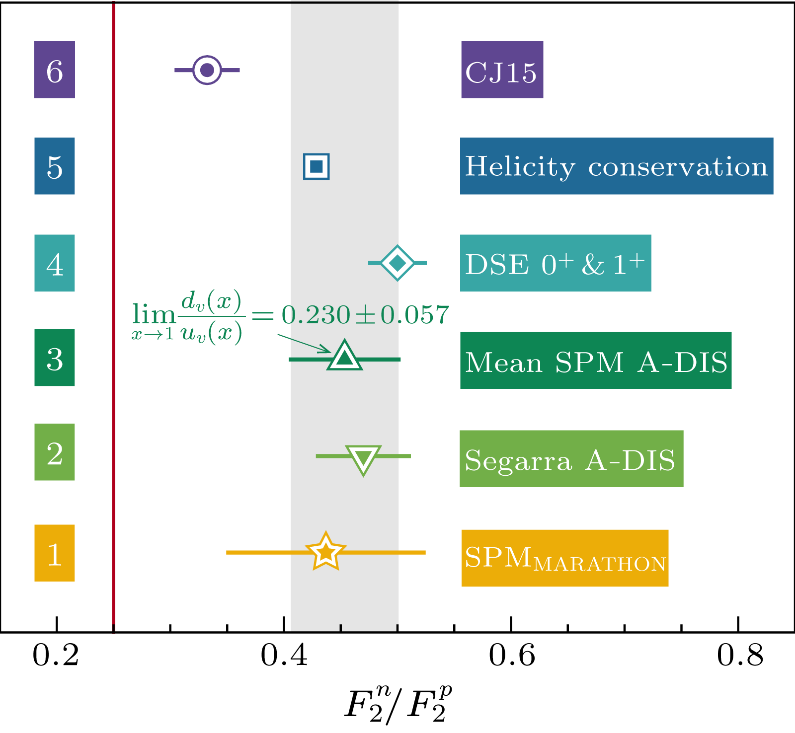
Figure 1. limx→1F2n(x)/F2p(x). MARATHON-based SPM prediction compared with results inferred from: nuclear DIS; Dyson–Schwinger equation analyses (DSE); quark counting (helicity conservation); and a phenomenological fit (CJ15). The vertical red line marks the physical lower limit on this ratio.
Valence Quark Ratio in the Proton
Research Backgrund
The proton is a bound state of three valence quarks, 1 down (d) and 2 up (u). At large values of the Bjorken scaling variable, which equates to a quark’s fraction of the proton’s total momentum, the in-proton d-quark/u-quark ratio of number-densities defines what is meant by a valence quark, i.e., what most people really think of when they hear the word “quark”. Despite the simple 1:2 ratio of valence-quark numbers, owing to the character of quantum field theory, the d/u ratio needs not be ½. Thus, determining the ratio’s value has been the subject of intense experimental and theoretical effort for almost 50 years.
Brief Introduction
An international team, joining physicists in China, Germany, and Italy, introduced a new mathematical technique – the Schlessinger point method (SPM) – into the analysis of data collected in deep inelastic scattering experiments on light mirror nuclei. Specifically designed to ensure extraction of all objective information contained in the data, the approach is also mathematically guaranteed to deliver a robust extrapolation onto any unmeasured domain with a sound estimate of uncertainty at each point. The result, shown in Fig. 1, is the first model-independent prediction for the neutron-to-proton structure function ratio that extends onto the crucial valence-quark domain: limxB→1F2n(xB)/F2P(xB)=0.454(47).
Research Significance
This study opens the door to new insights into the character of the proton, Nature’s most fundamental bound state, which lies at the core of atoms and defines nuclear physics. It emphasizes the role of two types of complex quark+quark correlations within the proton and establishes with a 99.999986% level of confidence that the proton wave function contains both such correlations. This is a very tight constraint on proton structure theory, which can be used to eliminate many existing models. Further, in establishing the importance of such correlations, it shows that hadron structure studies have many similarities with bound state problems in other areas of physics.
原文链接
HTML
研究快讯集锦
高混合熵提升非晶合金的能量状态
在可调耦合超导量子比特中实现全微波脉冲的CZ门
BaO/SrTiO3界面的电输运性质研究
高通量第一性原理计算探索潜在的笼目材料
氮的高压等结构相变
轨道转移矩驱动的垂直磁化无外场翻转
氟取代高分子在宏观和微观尺度上疏水特性的差异
Kitaev量子自旋液体候选材料α-RuCl3中分数化磁激发的证据
碳纳米管中的氮纳米管
赝厄米性保护幺正散射
非厄米反常贝里联络诱导的奇异输运现象
室温下自旋轨道转矩产生的20纳米斯格明子
Pauli Radius of the Proton
热还原氧化石墨烯膜中意外的锂选择性吸收
基于量子态的深度机器学习实现哈密顿量精确估计
重稀土氢化物的高温超导电性
多功能量子存储器
众里寻他千百度—量子磁体微观模型的多体计算自动寻参
量子自旋液体候选材料中低能激发的非局域效应
PT对称性诱导的激光阈值环及嵌在环上的连续谱中束缚态
半导体中掺杂行为随应变变化的基本规律
典型半导体材料在剪切应变下的本征超导电性
磁场中自旋轨道耦合系统的拓展Rashba解析近似方法研究
利用核四极矩共振和核磁共振研究笼目晶格超导体CsV3Sb5
库伦作用无尽期,动量蒙卡寄相思
二维金属硫代磷化物中的强磁电耦合效应
锶原子光晶格钟上的弗洛凯精密调控:拉比谱及灵敏度
Kagome化合物CsV3Sb5单晶超导态的各向异性
CsV3Sb5中高度稳定的超导再进入现象

点此浏览所有Express Letters
CPL Express Letters栏目简介
为了保证重要研究成果的首发权和显示度,CPL于2012年6月开设了Express Letters栏目。此栏目发表速度快,学术质量高。截至2020年底,平均每篇被引用约20次,已经在国内物理学界建立起良好口碑与声望,来稿数量不断增加。

https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-3426263-1335332.html
上一篇:研究快讯 | α-CsPbI3的缺陷容忍性:高温相材料中点缺陷性质的计算方法
下一篇:CPL亮点文章 | 2022年第4期