博文
《物理世界》研究进展: 磁场竟可翻转材料热膨胀系数
|

EXPRESS LETTER
Magnetic-Field-Induced Sign Changes of Thermal Expansion in DyCrO4
Jin-Cheng He (何金城), Zhao Pan (潘昭), Dan Su (苏丹), Xu-Dong Shen (申旭东), Jie Zhang (张杰), Da-Biao Lu (卢达标), Hao-Ting Zhao (赵浩婷), Jun-Zhuang Cong (丛君状), En-Ke Liu (刘恩克), You-Wen Long (龙有文), and Young Sun (孙阳)
Chin. Phys. Lett. 2023, 40 (6): 066501
DOI: 10.1088/0256-307X/40/6/066501
研究快讯
利用外加磁场调控材料的热膨胀系数
首次在不同结构的DyCrO4中,利用外加磁场实现了将常压锆石型z-DyCrO4的热膨胀系数由负变为正,高压白钨矿型s-DyCrO4的热膨胀系数由正变负再变成正的转变,为调控材料的热膨胀系数提供了一种全新策略。
This work has been highlighted in a research update published in Physics World.
Applied magnetic field flips a material’s thermal expansion
Isabelle Dumé
(Courtesy: iStock/enot-poloskun)
Most materials expand when heated. A few, such as water just above freezing, contract. Now, for the first time, physicists have found a material that switches from expanding to contracting in the presence of an applied magnetic field. The discovery of this field-induced sign change could offer a new way of controlling a material’s thermal expansion – a prospect that would have many industrial applications as well as interest for fundamental research.
In devices made from many different materials, any mismatch in how these materials behave when heated – their positive or negative coefficients of thermal expansion (CTEs) – can have important and sometimes unwanted consequences. For example, a component that combines materials with very different CTEs may be prone to deforming, cracking or otherwise failing when the temperature changes.
Since this effect is ultimately due to different atoms vibrating at different frequencies, it is sometimes possible to tune the size of the CTE by substituting one element for another in the material’s chemical formula. However, for most materials, this chemical substitution process is very limited in its scope.
From negative to positive
Using external variables such as magnetic or electric fields to tune a material’s CTE would be much more flexible than chemical substitution, and researchers had previously shown that this was possible with certain magnetic materials. In those studies, however, only the magnitude of the CTE had changed with magnetic field, not its sign.
In the new work, a team led by Youwen Long prepared a rare-earth chromate, DyCrO4, in two isomorphic phases: a zircon-type phase and a scheelite-type phase. The first of these phases was created using standard solid-state annealing at ambient pressure, while the second used high-pressure annealing. To their surprise, the researchers found that for both phases, the sign of the CTE changes when a magnetic field is applied.
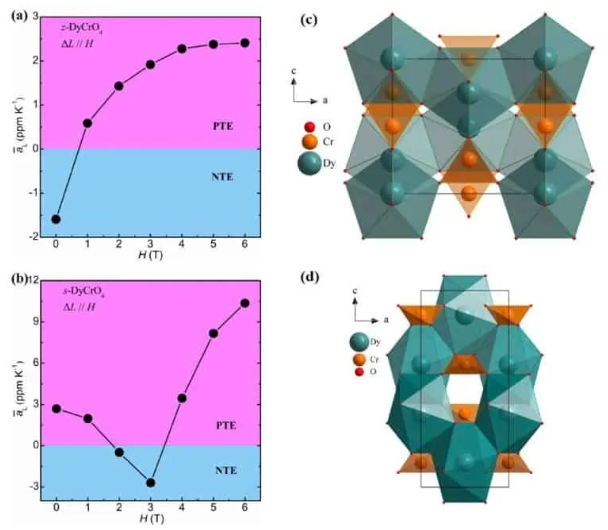
This figure shows the average linear coefficient of thermal expansion of (a) z-type DyCrO4 at 3-23 K and (b) s-type DyCrO4 at 3-24 K in a series of magnetic fields applied along the direction of sample length. Also included are a schematic diagram of the crystal structure of (c) z-type DyCrO4 and (d) s-type DyCrO4. (Courtesy: Y Long)
At zero magnetic field, Long explains that zircon-type DyCrO4 exhibits a negative CTE at temperatures below the ferromagnetic order temperature of 23 K. When they increased the magnetic field to 1.0 T, however, the CTE turned positive. In the scheelite phase, a magnetic field of up to 2.0 T can switch the initially positive CTE to negative. What is more, a “reentrant positive” CTE can be induced by increasing the field further, up to and over 3.5 T.
The researchers say that this is the first time anyone has observed a magnetic-field-induced change in the sign of a material’s CTE. “Our study provides the first example where external magnetic fields can significantly change the thermal expansion, including the magnitude and especially the sign, opening up a new avenue to readily control the thermal expansion beyond conventional chemical substitution,” they report. “We believe that our work will be of broad interest in fundamental and applied material sciences.”
According to Long, the anomalous effect stems from the unusually strong spin-lattice coupling in DyCrO4, and it could have broad applications in applied materials science. “One immediate application area, for example, might be to control the CTE of permanent magnet motors,” he tells Physics World.
The researchers are now exploring the possibility of using magnetic fields to tune the CTE in other magnetic functional materials, to see whether this could be a universal method for regulating their CTEs. They detail their present work in Chinese Physics Letters.
© Copyright 2023 IOP Publishing Ltd
研究快讯集锦
二维半导体包覆和范德华接触的晶体管构筑方法
基于斯塔克效应实现单个铒离子发光的大范围调谐
利用超快激光在单层MoS2中产生可由声子调控的磁性
水热法获得无间隙Fe的铁基超导体FeSe0.2Te0.8单晶
使用频率可调的抗磁悬浮探测器寻找超轻暗物质
扭角双层GaTe中的光学可调控的摩尔激子
利用外加磁场调控材料的热膨胀系数
多组份玻色超流系统的流体力学
超导系统中实现非阿贝尔任意子的量子模拟
钽基富氢化物高压合成和高压超导的发现
利用解纠缠张量强化密度矩阵重整化群算法
基于第一性原理计算的Lu-H-N相图
基于范德华A型反铁磁CrSBr的自旋过滤隧道结中的巨大隧穿磁电阻
双层1T-TiSe2中的电子-激子耦合
Fe基Kagome晶格化合物单晶Y0.5Fe3Sn3的结构确定、非稳反铁磁态及输运行为
π介子质量分布的实验确定
700 Wh/kg锂二次软包电池
转角四层二硫化钼莫尔超晶格中铁电序与关联态的耦合
LuH2压力诱导的颜色变化
门电压可调的细直径InAs-Al纳米线超导量子比特
手性磁畴壁调控量子反常霍尔效应
“12442”型铁基超导体RbCa2Fe4As4F2中奇异的第二峰效应
利用时间合成维度构建光学神经网络
基于随机态含时演化的大尺度密度泛函理论计算方法
插层铁基(Li,Fe)OHFeSe:准二维高Tc超导电性
强场电离诱导的电子-空穴相干性实时测量
含记忆临界现象理论
光学克尔非线性谐振腔中的动态非互易
范德华铁磁/半导体异质结中的大室温磁电阻
准二维铁硒基超导体中普适赝能隙行为的核磁共振实验证据
兆巴高压下的金刚石NV中心光探磁共振
在超导量子电路中演示非阿贝尔系统的量子几何张量测量
基于里德堡原子基态封锁的双量子比特几何门
SrTiO3单晶立方相到四方相转变引起的弹性异常
氮化二聚钴:一类潜在的新型高温超导材料
Manakov方程中调制不稳定性和非简并Akhmediev呼吸子
表面粗糙的聚集和反聚集效应对电子隧穿的巨大影响
对数量子时间晶体
本征微观态的重整化群理论
伊辛模型的几何上临界维度
通过氢化钙退火方法连续掺杂Bi2212至电子掺杂超导体
氦离子注入制备的钇钡铜氧高温超导约瑟夫森结
变分角转移矩阵重正化群方法及其在经典统计模型中的应用
在单比特上基于量子态判别的互文性实验验证
巨行星内部可能存在的氦-二氧化硅化合物
范德瓦尔斯超导材料中准二维超导电性和可调控近藤晶格的共存
QCD强耦合常数在微扰及非微扰能区跑动行为的新分析
始于生成网络的马尔可夫链蒙卡
压力诱导具有超高能量密度的含氖聚合氮化物
FeSe超导体的反常能带劈裂和强各向异性超导能隙随掺硫的奇异演变
锁相热扩散趋肤效应
用于拓扑量子器件的纯相超细InAs–Al纳米线原位分子束外延
α-CsPbI3的缺陷容忍性:高温相材料中点缺陷性质的计算方法
Valence Quark Ratio in the Proton
高混合熵提升非晶合金的能量状态
在可调耦合超导量子比特中实现全微波脉冲的CZ门
BaO/SrTiO3界面的电输运性质研究
高通量第一性原理计算探索潜在的笼目材料

点此浏览所有Express Letters
CPL Express Letters栏目简介
为了保证重要研究成果的首发权和显示度,CPL于2012年6月开设了Express Letters栏目。此栏目发表速度快,学术质量高。截至2020年底,平均每篇被引用约20次,已经在国内物理学界建立起良好口碑与声望,来稿数量不断增加。

收录于合集 #Updates in Physics World 3上一篇阅读原文
https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-3426263-1394624.html
上一篇:CPL影响力再上新台阶 | IF=3.5
下一篇:研究快讯 | 基于电子体系的高随机性高稳定性的无后处理量子随机数发生器