博文
新型、更坚固、可循环的塑料
 精选
精选
||
新型、更坚固、可循环的塑料
诸平

白色革命带来的白色污染已经成为全球面临的一个严重的环境污染难题。塑料垃圾无处不在,环境污染难题亟待破解。据德国康斯坦茨大学(University Of Konstanz, Universitätsstraße, Germany)2023年2月19日报道,该校的研究人员与BASF公司(BASF SE, PMD/GB—B001, Carl-Bosch-Strasse, Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Germany)的研究人员合作,已经开发出一种新型、更坚固、可回收的塑料(A New, Stronger and Recyclable Plastic)。这是一种可生物降解的聚酯((biodegradable polyester)),其性能可与高密度聚乙烯(high-density polyethylene)相媲美。
聚乙烯以其许多优点而闻名,但其缺乏生物降解性一直是一个挑战。然而,一组研究人员现在已经解决了这个问题,他们发明了一种塑料,这种塑料具有与聚乙烯类似的热塑性塑料性能,而且是可生物降解的。该研究小组的相关研究结果于2022年12月8日已经在德国《应用化学国际版》(Angewandte Chemie International Edition)杂志网站发表——Marcel Eck, Simon Timm Schwab, Taylor Frederick Nelson, Katrin Wurst, Steffen Iberl, David Schleheck, Christoph Link, Glauco Battagliarin, Stefan Mecking. Biodegradable High-Density Polyethylene-like Material. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, February 1, 2023, 62(6): e202213438. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202213438. First published: 08 December 2022. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202213438. 此文介绍说,这种新材料是一种可以通过温和的化学或生物过程完全分解成原始成分的半结晶聚酯(semicrystalline polyester)。
高密度聚乙烯(High-density polyethylene简称HDPE)是一种特别坚固耐用的材料。它的热塑性特性得益于其分子链的内部结构,这些分子链以结晶方式排列,范德华力(van der Waals forces)会增加吸引力。分子链也是纯碳氢化合物。结晶度和碳氢化合物含量的结合意味着,可能能够降解塑料的微生物无法进入塑料链并将其分解。
德国康斯坦茨大学的斯蒂芬·麦克林(Stefan Mecking)研究小组和他的同事们已经开发出一种聚酯,它的结晶度与HDPE相似,而且还保留了有益的机械性能。与聚乙烯不同,聚酯还含有理论上可以通过化学或酶降解的官能团。然而,在正常情况下,聚酯的结晶度越高(即与HDPE越相似),其就越不容易被生物降解。
因此,研究小组惊讶于晶体聚酯在暴露于酶的情况下降解的速度之快。“我们测试了天然酶的降解速度,比我们的参考材料快了一个数量级,”斯蒂芬·麦克林解释道。不仅仅是酶溶液能降解聚酯,土壤微生物也能完全降解此类聚酯。
但是,是什么让这种聚酯纤维具有如此出色的生物降解性?该团队能够确定乙二醇(ethylene glycol)的重要作用,乙二醇是聚酯的基本成分之一。斯蒂芬·麦克林补充道:“这种结构单元实际上在聚酯纤维中很常见。它的熔点很高,但也增加了类似聚乙烯的材料的降解性。”
由于其良好的化学和生物降解性以及机械性能,这种新型聚酯可作为可回收热塑性材料应用,对环境的影响最小。斯蒂芬·麦克林补充说,最终目标是实现闭环化学循环,将塑料分解成原材料,生产新塑料。该团队使用这种塑料的另一个好处是,即使有任何材料进入了环境,它们也能生物降解,不会留下持久的影响。
该研究由欧洲研究委员会(European Research Council简称ERC, Advanced Grant DEEPCAT, No. 832480)资助。
上述介绍,仅供参考。欲了解更多信息,敬请注意浏览原文或者相关报道。
While it resembles high density polyethylene with regard to its mechanical properties and solid-state structure and has a high melting point (Tm=96 ℃), the novel polyester-2,18 material at the same time fully hydrolyzes in in vitro enzymatic degradation studies and mineralizes under industrial composting conditions (ISO standard 14855-1) within two months.
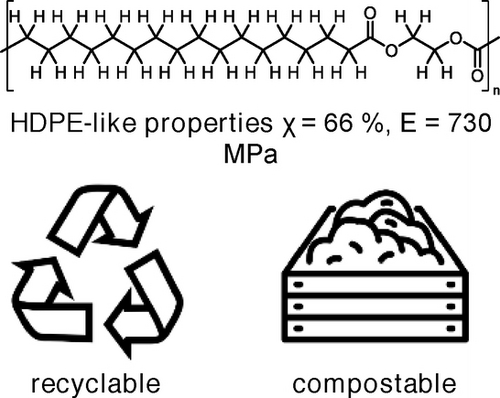
We report a novel polyester material generated from readily available biobased 1,18-octadecanedicarboxylic acid and ethylene glycol possesses a polyethylene-like solid-state structure and also tensile properties similar to high density polyethylene (HDPE). Despite its crystallinity, high melting point (Tm=96 ℃) and hydrophobic nature, polyester-2,18 is subject to rapid and complete hydrolytic degradation in in vitro assays with isolated naturally occurring enzymes. Under industrial composting conditions (ISO standard 14855-1) the material is biodegraded with mineralization above 95% within two months. Reference studies with polyester-18,18 (Tm=99 ℃) reveal a strong impact of the nature of the diol repeating unit on degradation rates, possibly related to the density of ester groups in the amorphous phase. Depolymerization by methanolysis indicates suitability for closed-loop recycling.
https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-212210-1377230.html
上一篇:这款“哈利波特”光传感器实现了200%的神奇高效率
下一篇:地球物理学家Rob Govers回答土、叙地震的有关提问