博文
Molecular Plant:QTL精细作图提速新方法~QTG-seq
|||
QTG-seq accelerates QTL fine mapping through QTL partitioning and whole-genome sequencing on bulked segregant samples
First author: Hongwei Zhang; Affiliations: Institute of Crop Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (中国农科院作物所): Beijing, China
Corresponding author: Lin Li
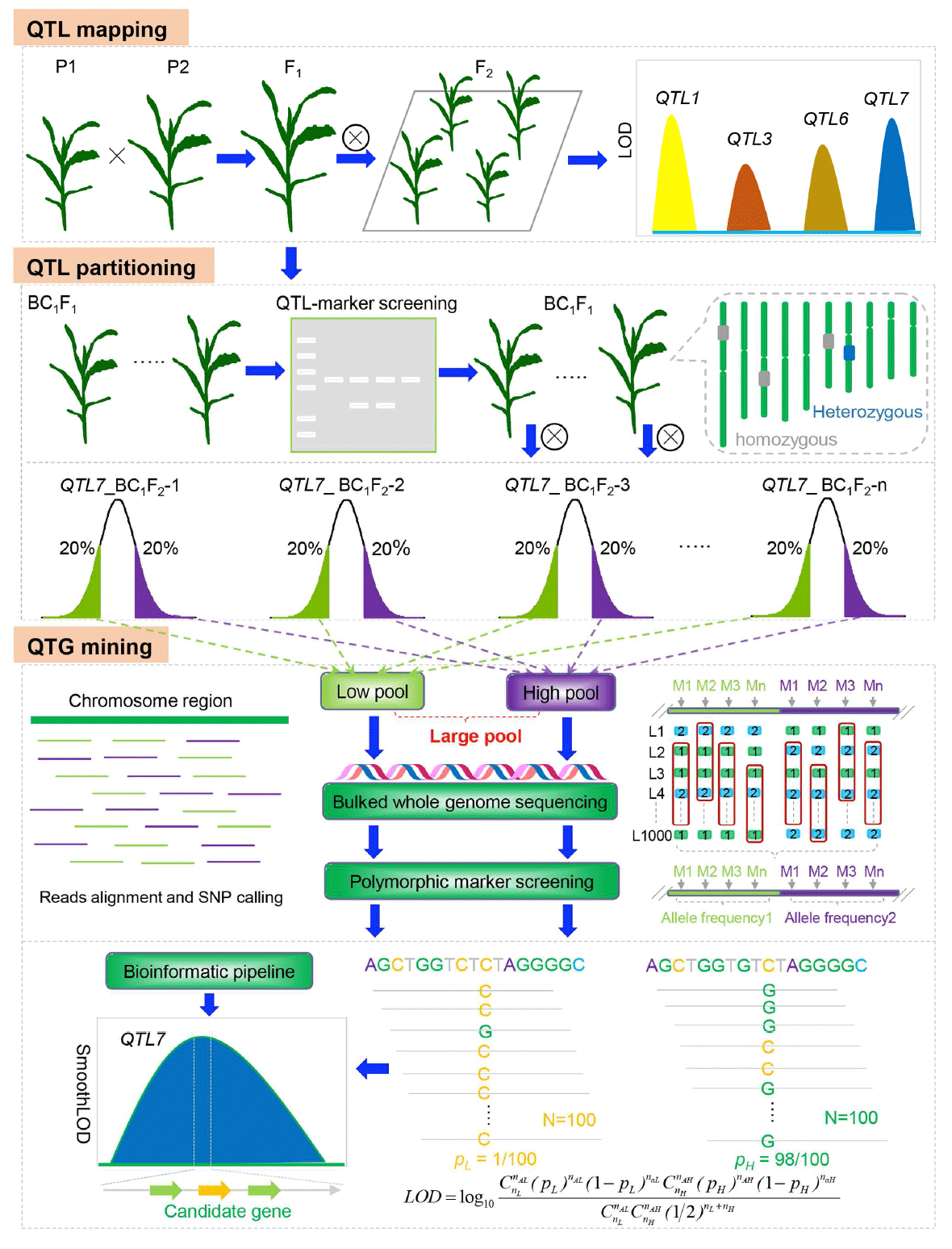
Deciphering the genetic mechanisms underlying agronomic traits is of great importance for crop improvement. Most of these traits are controlled by multiple quantitative trait loci (QTL), and identifying the underlying genes by conventional QTL fine-mapping is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Here, we devised a new method named quantitative trait gene sequencing (QTG-seq) to accelerate QTL fine mapping. QTG-seq combines QTL partitioning to convert a quantitative trait into a near-qualitative trait, bulked segregant sequencing on a large segregating population, and a robust new algorithm for identifying candidate genes. Using QTG-seq, we fine-mapped a plant height QTL in maize (Zea mays L.), qPH7, to a 300-kb genomic interval and verified that a gene encoding an NF-YC transcription factor was the functional gene. Functional analysis suggested that qPH7 might influence plant height by interacting with proteins encoded by a CO-like gene and an AP2 domain containing gene. Selection footprint analysis indicated that qPH7 was subject to strong selection during maize improvement. In summary, QTG-seq provides an efficient method for QTL fine-mapping in the era of “big data”.
解析农艺性状潜在的遗传调控机制对于作物的育种改良来说是至关重要的。大多数的农艺性状是由多个数量性状位点QTL所控制的,而通过传统的QTL精细作图的方法来鉴定这些农艺性状潜在的控制基因费时费力。本文,作者开发出了一套叫做数量性状基因测序QTG-seq的新方法来加速QTL精细作图。QTG-seq整合了能够将一个数量性状转化成一个近等质量性状的QTL分离技术、一个大的分离群体的集团分离测序以及一个新的鉴定候选基因的算法。通过QTG-seq,作者在玉米中将一个控制植株高度的QTL qPH7精细定位到了一段300kb的基因组序列区域,并且鉴定到了该区域的一个编码NF-YC转录因子的基因是控制植株高度的功能基因。功能分析显示qPH7可能通过与一个CO-like基因编码的蛋白以及一个含有AP2结构域基因所编码的蛋白发生互作来影响植株的高度。选择足迹分析显示qPH7在玉米驯化过程中受到了强烈的选择。综上,QTG-seq作为一个有效的方法可以在大数据时代加速QTL精细作图。
通讯:李林 (http://cpst.hzau.edu.cn/info/1015/1638.htm)
个人简介:2001-2005年,中国农业大学,农学与生物技术学院,遗传育种专业,学士;2005-2010年,中国农业大学,农学与生物技术学院,遗传育种专业,博士;2010-2013年,美国明尼苏达大学双城分校,博士后;2013-2015年,美国明尼苏达大学双城分校,研究助理;2015-至今,华中农业大学植物科学技术学院教授,作物遗传改良国家重点实验室PI,玉米研究团队成员。
研究方向:玉米野生资源利用-大规模群体构建、进化与重要性状关键基因克隆、及基因克隆新技术与新方法开发与利用等;玉米与其近缘种大刍草株型性状比较功能基因组学研究;玉米与其近缘种大刍草基因组功能元件(long noncoding RNA,circular RNA等)注释、调控网络研究。
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2018.12.018
Journal: Molecular Plant
Accepted date: 24 December, 2018
https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-3158122-1155077.html
上一篇:Nature Plants:向日葵的泛基因组分析
下一篇:Plant Physiology:复苏植物的协同演化
全部作者的其他最新博文
- • Plant Physiology:CsMADS3促进柑果中的叶绿素降解和类胡萝卜素合成(华中农业大学)
- • Molecular Plant:LBD11-ROS反馈调节作用于拟南芥的维管形成层增殖和次生生长(浦项科技大学)
- • Science Advances:根结线虫通过调控植物的CLE3-CLV1模块,促进侵染进程(日本熊本大学)
- • The Plant Cell:拟南芥P小体组分通过对FLC的转录调控,影响开花时间(安徽农业大学)
- • Nature Communications:油菜素内酯参与植物营养生长期转变的分子机制解析(浙江农林大学)
- • Current Biology:光合作用产生的蔗糖驱动侧根“生物钟”(德国弗莱堡大学)