博文
Current Biology:地钱DELLA具有类似于被子植物中协调生长与胁迫抗性的功能
||
Coordination between growth and stress responses by DELLA in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha
第一作者:Jorge Hernández-García
第一单位:巴仑西亚理工大学
通讯作者:Miguel A. Blázquez
Abstract
背景回顾:Plant survival depends on the optimal use of resources under variable environmental conditions. Among the mechanisms that mediate the balance between growth, differentiation, and stress responses, the regulation of transcriptional activity by DELLA proteins stands out. 被子植物:In angiosperms, DELLA accumulation promotes defense against biotic and abiotic stress and represses cell division and expansion, while the loss of DELLA function is associated with increased plant size and sensitivity toward stress. Given that DELLA protein stability is dependent on gibberellin (GA) levels and GA metabolism is influenced by the environment, this pathway is proposed to relay environmental information to the transcriptional programs that regulate growth and stress responses in angiosperms. 苔藓植物:However, DELLA genes are also found in bryophytes, whereas canonical GA receptors have been identified only in vascular plants. Thus, it is not clear whether these regulatory functions of DELLA predated or emerged with typical GA signaling. 结果1:Here, we show that, as in vascular plants, the only DELLA in the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha also participates in the regulation of growth and key developmental processes and promotes oxidative stress tolerance. 结果2:Moreover, part of these effects is likely caused by the conserved physical interaction with the MpPIF transcription factor. 结论:Therefore, we suggest that the role in the coordination of growth and stress responses was already encoded in the DELLA protein of the common ancestor of land plants, and the importance of this function is underscored by its conservation over the past 450 million years. 摘 要 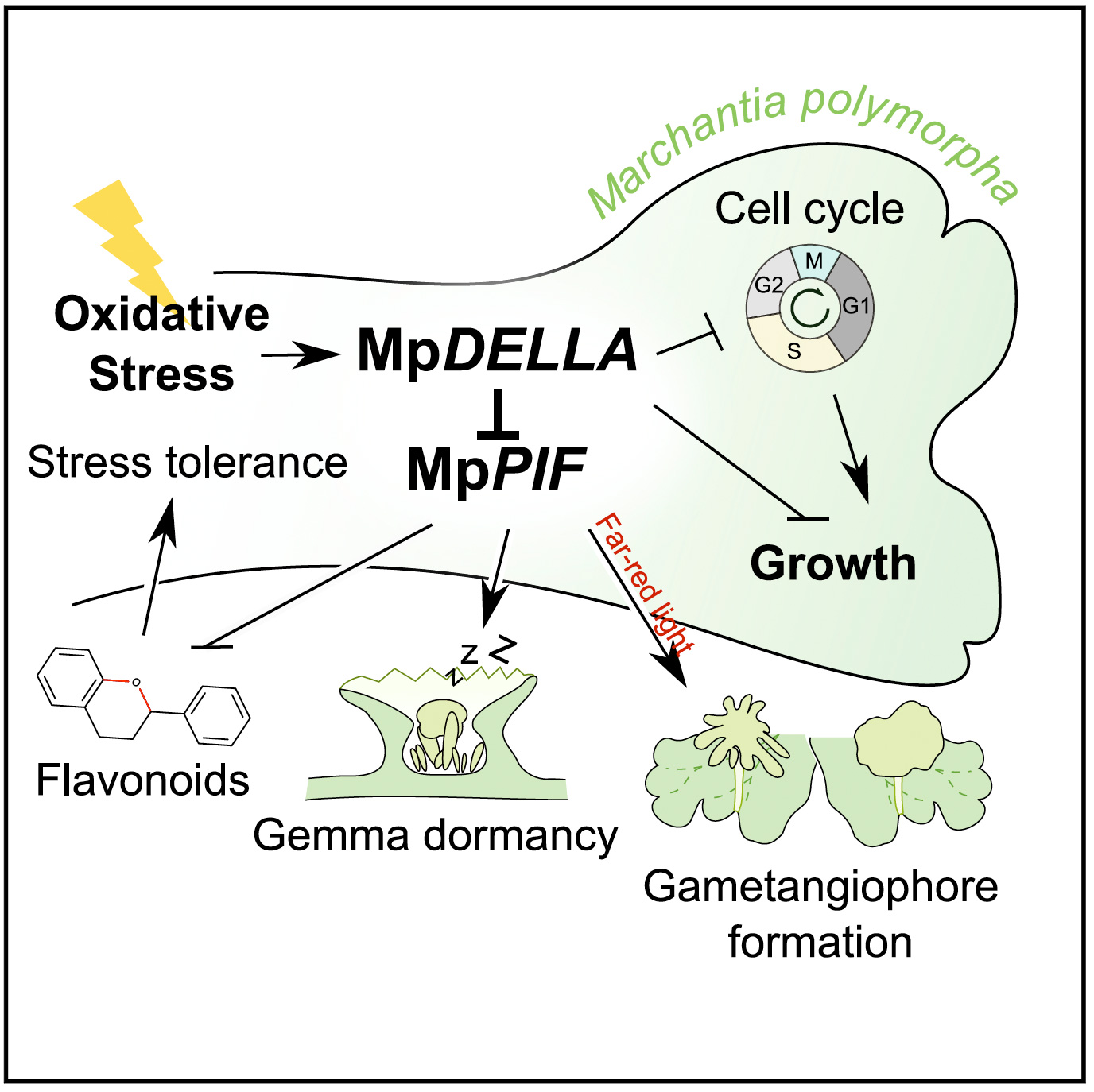
植物的生存依赖于在不断变化的环境条件下对资源的最佳利用。在介导生长、分化和胁迫响应之间平衡的机制中,DELLA蛋白对转录活性的调控尤为突出。在被子植物中,DELLA的积累促进了对生物和非生物胁迫的防御,抑制了细胞分裂和扩张,而DELLA功能的丧失则与植株大小的增加和对胁迫的敏感性有关。鉴于DELLA蛋白的稳定性依赖于赤霉素(GA)的水平,而GA的代谢受环境的影响,这一途径被认为是将环境信息传递给调节被子植物生长和胁迫响应相关转录程序。然而,苔藓植物中也发现了DELLA基因,而典型的GA受体仅在维管植物中发现。因此,目前尚不清楚DELLA的这些调节功能是否早于或随着典型GA信号转导一起出现。本文中,作者发现与维管植物一样,地钱中唯一的DELLA也参与对其生长和关键发育过程的调节,并促进氧化胁迫的耐受性。此外,这些效应的一部分可能是由DELLA与MpPIF转录因子之间保守的物理相互作用所介导的。因此,作者提出DELLA蛋白中在协调生长和胁迫响应中的功能已经在陆地植物共同祖先中存在,并且这一功能的重要性在过去4.5亿年的演化中得到了充分的彰显。
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2021.06.010
Journal: Current Biology
Published date: July 01, 2021
https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-3158122-1293905.html
上一篇:Current Biology:植物叶片挥发性物质演化的驱动因子
下一篇:Science:拟南芥绒毛层产生的siRNAs决定了父本生殖细胞中的表观遗传
全部作者的其他最新博文
- • Plant Physiology:CsMADS3促进柑果中的叶绿素降解和类胡萝卜素合成(华中农业大学)
- • Molecular Plant:LBD11-ROS反馈调节作用于拟南芥的维管形成层增殖和次生生长(浦项科技大学)
- • Science Advances:根结线虫通过调控植物的CLE3-CLV1模块,促进侵染进程(日本熊本大学)
- • The Plant Cell:拟南芥P小体组分通过对FLC的转录调控,影响开花时间(安徽农业大学)
- • Nature Communications:油菜素内酯参与植物营养生长期转变的分子机制解析(浙江农林大学)
- • Current Biology:光合作用产生的蔗糖驱动侧根“生物钟”(德国弗莱堡大学)