博文
[转载]CPB封面文章和亮点文章 | 2023年第9期
||
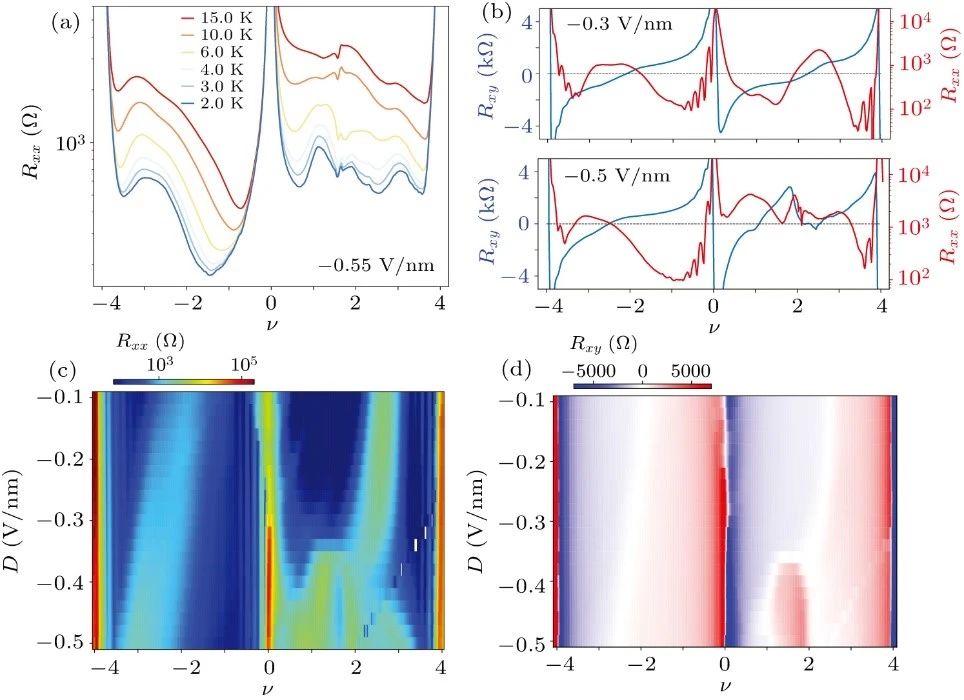
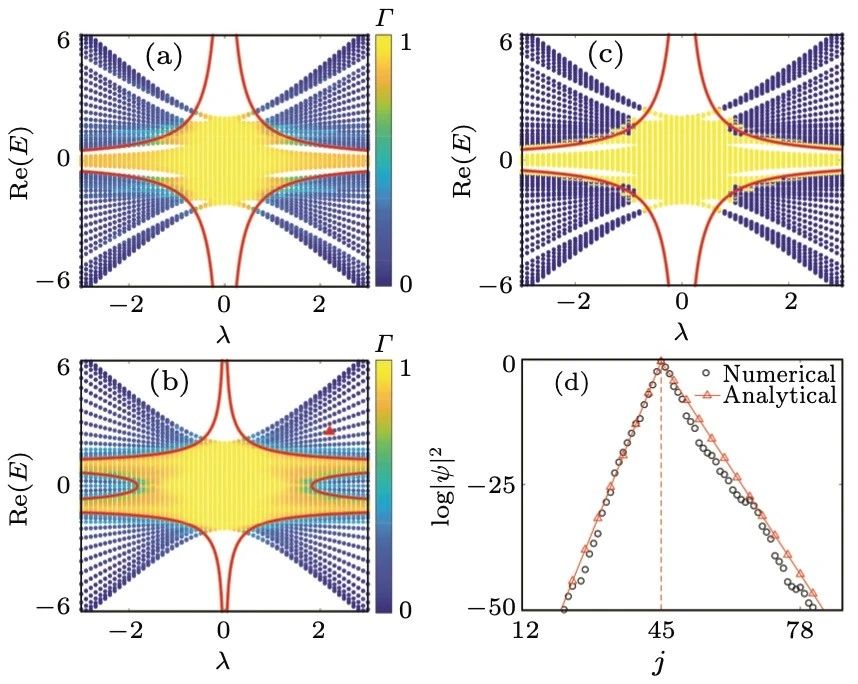
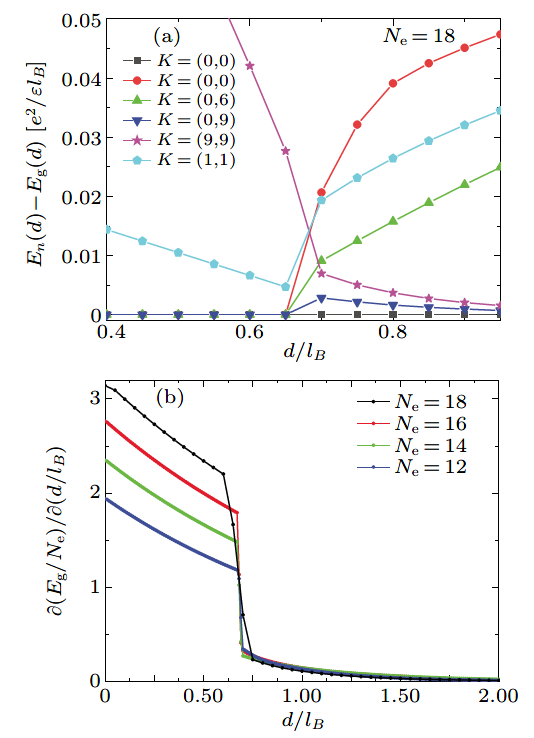
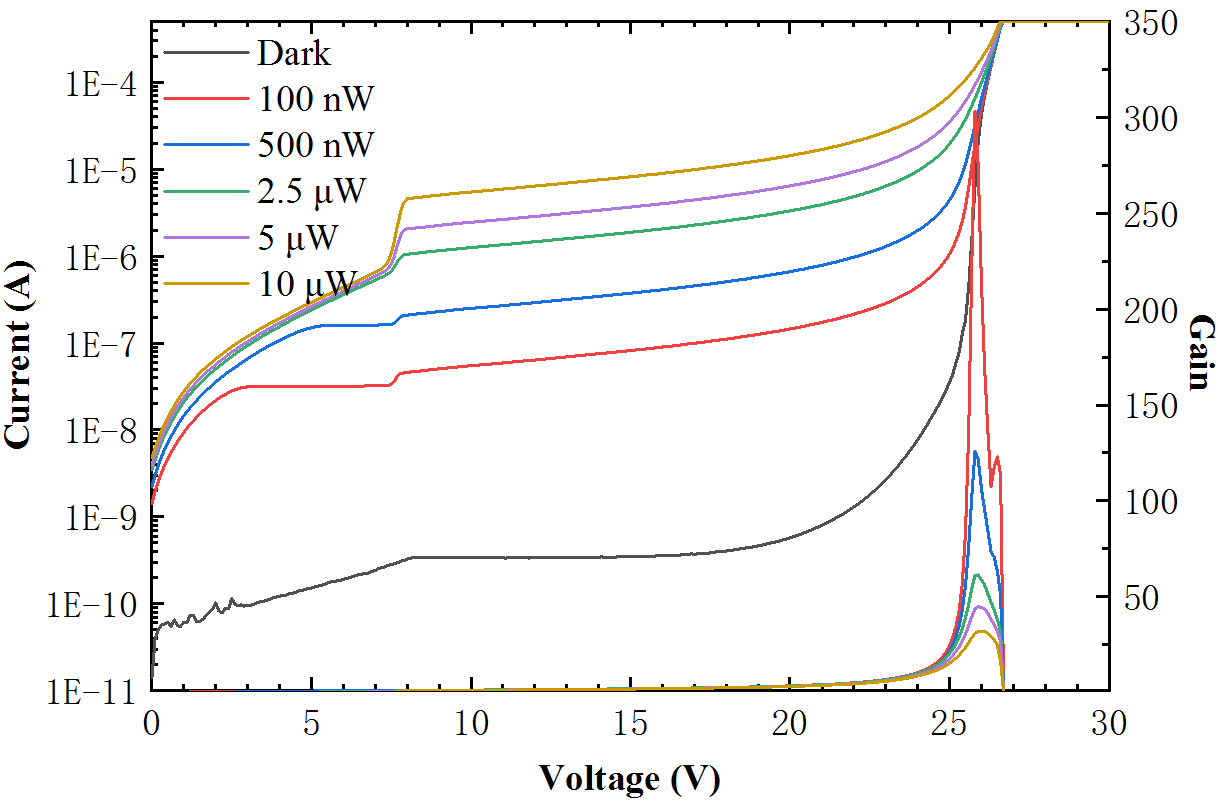
封面文章 Emergence of correlations in twisted monolayer-trilayer graphene heterostructures Zhang Zhou(周璋), Kenji Watanabe, Takashi Taniguchi, Xiao Lin(林晓), Jinhai Mao(毛金海), and Hong-Jun Gao(高鸿钧) Chin. Phys. B, 2023, 32 (9): 097203 文章亮点介绍石墨烯的莫尔电子体系正发展为调控新型量子态的重要平台。转角双层石墨烯作为最简单的结构,在理论和实验上都显示出有效构建平带的特性。直觉上这个图像也适用于转角多层石墨烯,转角(M +N)层石墨烯将在M层和N层之间的界面处出现两个低能平带。将这个概念扩展到转角多层石墨烯异质结有望创造更丰富的关联态,因为体系的对称性和能带结构发生了改变。 在这项工作中,我们研究了转角单层-三层石墨烯异质结(Bernal堆叠三层)的电输运特性。我们观察到全填充(ν = ± 4)处的电阻峰,并且电阻极大值区域高度依赖于电荷密度和电位移场。在转角为1.45°的样品中,在高位移场(D < -0.3 V/nm)下,我们发现了莫尔超晶格整数填充(ν = 1, 2)处的关联相,并且其在一定磁场(> 0.04ϕ0,ϕ0代表莫尔超晶格的磁通量子)下得到稳定。更进一步,我们从扫描磁场的朗道扇图中观察到关联态的简并打开。我们的结果展示了莫尔工程在转角单层-三层石墨烯中的有效性,并为电场可调关联相提供了参考,将推动对转角多层石墨烯的更深入研究。 原文链接 PDF Fig. 3. Tunable band structure and transport properties of the tMTG device with θ = 1.45°. (a) Rxx as a function of the filling factor at D = −0.55 V/nm at a series of temperatures from 15 K to 2 K at B = 0. (b) Rxx (red) and Rxy (blue) as a function of the filling factor at D = −0.3 V/nm (top panel) and −0.5 V/nm (bottom panel) and B = 2.0 T. The horizontal dashed lines indicate Rxy = 0. (c), (d) Mapping of Rxx (c) and Rxy (d) on the filling factor and displacement field at an external magnetic field B = 2.0 T and temperature T = 2.0 K. 亮点文章 Sheng-Lian Jiang(蒋盛莲), Yanxia Liu(刘彦霞), and Li-Jun Lang(郎利君) Chin. Phys. B, 2023, 32 (9): 097204 文章亮点介绍 无序/准无序系统中扩展态到局域态的转变一直是大家关注的焦点。在一维系统中此类转变通常与能量无关,因此寻找或构建具有能量依赖的扩展-局域相变(即迁移率边)的模型便成为一个重要的研究方向。此类模型的能谱往往被迁移率边分割成扩展区和局域区(有时还有介于两者之间的临界区)。近些年非厄米物理快速发展,最近对迁移率边的研究开始由厄米系统扩展到非厄米系统。如何寻找或构建具有迁移率边的非厄米模型并求解同样成为这个领域的一个核心问题。对于一维厄米准无序系统,早期主流的方法是通过寻找自对偶点确定迁移率边;而当扩展到相应的非厄米系统时,此方法不再适用,通常需要利用Avila全局理论才能解析得到迁移率边。一个典型的例子就是一维马赛克模型。全局理论虽然是求解迁移率边很好的解析方法,但每个模型都需要进行较为复杂的计算和证明,在效率上较慢。 本文针对一维非厄米马赛克模型,将其与对应的非马赛克模型联系起来,建立了一种一般的映射关系。只要知道一维非厄米马赛克模型的相变点和李雅普诺夫指数的解析表达式,便可以根据映射关系直接得到相应马赛克模型的迁移率边和李雅普诺夫指数。依据此映射关系,并不需要对马赛克模型逐一计算便可得知一类一维非厄米马赛克模型的相变性质,大大提高了寻找具有迁移率边的非厄米模型的效率。本文的研究为寻找具有迁移率边的非厄米模型提供了新的方法。 原文链接 PDF Fig. 1. The fractal dimension Γ as a function of the real part of the eigenenergy Re(E) and a real potential strength λ, numerically calculated for the mosaic period (a) κ=2 and (b) κ=3 under periodic boundary conditions. (c) The existence or not of the imaginary part Im(E) of energy corresponding to (a), where (non)zeros of Im(E) are colored in blue (yellow). The red solid lines in (a)–(c) are the analytical mobility edges. (d) Comparison of a localized state marked by the red triangle in (b) with the corresponding analytical result, show that the two Lyapunov exponents can well characterize the asymmetric localization in the non-Hermitian Aubry-André-like mosaic model. The dotted line indicates the center site of localization. 亮点文章 Phase transition in bilayer quantum Hall system with opposite magnetic field Ke Yang(杨珂) Chin. Phys. B, 2023, 32 (9): 097303 文章亮点介绍 量子霍尔效应因其丰富且有趣的物理一直以来备受学者青睐。由双层量子霍尔系统实现的二分量分数量子霍尔态展现出更加新奇多样的拓扑相。这些相可以由成对复合粒子描述。以 υ=1/2+1/2 的双层量子霍尔系统为例,在层间距很小时可以观察到超流相,在层间距很大时可以观察到复合费米液体相。近年来,二维材料莫尔超晶格的研究中实现了近平带系统。在由二维转角石墨烯构成的双层摩尔超晶格中,研究者提出可以存在两个能带具有相反陈数的情况。这种状态可以等价为两个朗道能级上的粒子经历相反磁场,并在双层量子霍尔系统中实现。 基于以上考虑,我们使用精确对角化方法研究具有相反陈数、填充数 υ=1/2+1/2 的双层量子霍尔系统。我们映射系统为经历共同磁场的双层系统,但层间是吸引作用,层内有排斥作用。通过驱动层间距d/lB从零增长至层分离,我们观察到从激子条纹(exciton stripe)相到复合费米液体(CFL)相的量子相变,相变点在d/lB=0.68。我们认为带电粒子(电子/空穴)与磁通共同构成电子/空穴复合费米子(e/h-CF)。在层间距很小时,由于强层间吸引相互作用,不同层e-CF与h-CF紧紧绑在一起。复合费米子对形成激子,激子构成条纹相。在双层分离时,各层复合费米子分别构成复合费米液体。本研究可帮助我们理解双层束缚激子(Bound Exciton)凝聚的相图。 原文链接 PDF Fig. 2. Numerical evidence for the critical point. (a) The low energy levels are plotted against layer separation d/lB at different K sectors for Ne = 18. We show the energy level crossings between different K sectors at dc/lB. We set k=K•2π/Ns. (b) The first-order derivative curves of the ground-state energy Eg/Ne as a function of layer separation d/lB. 亮点文章 Planar InAlAs/InGaAs avalanche photodiode with 360 GHz gain×bandwidth product Shuai Wang(王帅), Han Ye(叶焓), Li-Yan Geng(耿立妍), Fan Xiao(肖帆), Yi-Miao Chu(褚艺渺), Yu Zheng(郑煜), and Qin Han(韩勤) Chin. Phys. B, 2023, 32 (9): 098507 文章亮点介绍 随着现代通讯的迅猛发展,人们对光纤通讯系统提出了更高的要求。高速、高灵敏度的光电探测器在光纤通讯中起到举足轻重的作用,其中雪崩光电探测器(APD)以其自带增益的属性在高速长距离光纤通讯中具有广阔的应用前景。InAlAs材料载流子离化率比值k较低,以InAlAs为APD的倍增材料可以获得更高的增益带宽积及更低的过剩噪声因子。InAlAs材料的禁带宽度较宽,有利于降低APD器件的隧穿暗电流,而且InAlAs作为倍增材料的APD器件的温度稳定性也更高。垂直入射结构APD可以比较容易的实现光耦合,而且在光信号吸收过程中不受偏振状态的影响。因此开展垂直入射高速InAlAs APD的研究具有非常重要的现实意义。 在本文中,我们研究了一种平面型垂直入射的InAlAs APD,该结构通过类似于传统InP APD的选择性Zn扩散工艺来制备。制备的InAlAs APD,暗电流在0.9倍击穿电压时为3 nA,单位响应度为0.4 A/W。同时实现了24 GHz的最大3 dB带宽和360 GHz的增益带宽积。这些特性证明了平面InAlAs APD在光通信系统中的应用潜力。 原文链接 PDF Fig. 4. The dark current, photocurrent and operation gain versus reverse bias of a 15 µm diameter Fig. 6. The high-frequency response versus multiplication factor. SPECIAL TOPIC — Plasma disruption SPECIAL TOPIC — Smart design of materials and design of smart materials SPECIAL TOPIC — Celebrating the 100th Anniversary of Physics Discipline of Xiamen University TOPICAL REVIEW — Physics in micro-LED and quantum dots devices TOPICAL REVIEW — Celebrating 30 Years of Chinese Physics B TOPICAL REVIEW — The third carbon: Carbyne with one-dimensional sp-carbon SPECIAL TOPIC — Fabrication and manipulation of the second-generation quantum systems SPECIAL TOPIC — Celebrating the 70th Anniversary of the Physics of Jilin University TOPICAL REVIEW—Laser and plasma assisted synthesis of advanced nanomaterials in liquids TOPICAL REVIEW — Progress in thermoelectric materials and devices SPECIAL TOPIC — Emerging photovoltaic materials and devices SPECIAL TOPIC — Organic and hybrid thermoelectrics SPECIAL TOPIC — Superconductivity in vanadium-based kagome materials SPECIAL TOPIC— Interdisciplinary physics: Complex network dynamics and emerging technologies SPECIAL TOPIC — Non-Hermitian physics SPECIAL TOPIC — Unconventional superconductivity SPECIAL TOPIC — Two-dimensional magnetic materials and devices SPECIAL TOPIC — Ion beam modification of materials and applications SPECIAL TOPIC — Quantum computation and quantum simulation SPECIAL TOPIC —Twistronics SPECIAL TOPIC — Machine learning in condensed matter physics SPECIAL TOPIC — Phononics and phonon engineering SPECIAL TOPIC — Water at molecular level SPECIAL TOPIC — Optical field manipulation SPECIAL TOPIC — Modeling and simulations for the structures and functions of proteins and nucleic acids SPECIAL TOPIC —Terahertz physics SPECIAL TOPIC — Ultracold atom and its application in precision measurement SPECIAL TOPIC — Topological 2D materials SPECIAL TOPIC — Active matters physics SPECIAL TOPIC — Physics in neuromorphic devices SPECIAL TOPIC — Advanced calculation & characterization of energy storage materials & devices at multiple scale TOPICAL REVIEW — Advanced calculation & characterization of energy storage materials & devices at multiple scale TOPICAL REVIEW — Quantum dot displays TOPICAL REVIEW — CALYPSO structure prediction methodology and its applications to materials discovery SPECIAL TOPIC — A celebration of the 100th birthday of Kun Huang TOPICAL REVIEW — A celebration of the 100th birthday of Kun Huang SPECIAL TOPIC — Strong-field atomic and molecular physics TOPICAL REVIEW — Strong-field atomic and molecular physics TOPICAL REVIEW — Topological semimetals SPECIAL TOPIC — Topological semimetals SPECIAL TOPIC — Photodetector: Materials, physics, and applications TOPICAL REVIEW — Photodetector: Materials, physics, and applications TOPICAL REVIEW — Fundamental research under high magnetic fields Virtual Special Topic — High temperature superconductivity Virtual Special Topic — Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 官网:http://cpb.iphy.ac.cn https://iopscience.iop.org/journal/1674-1056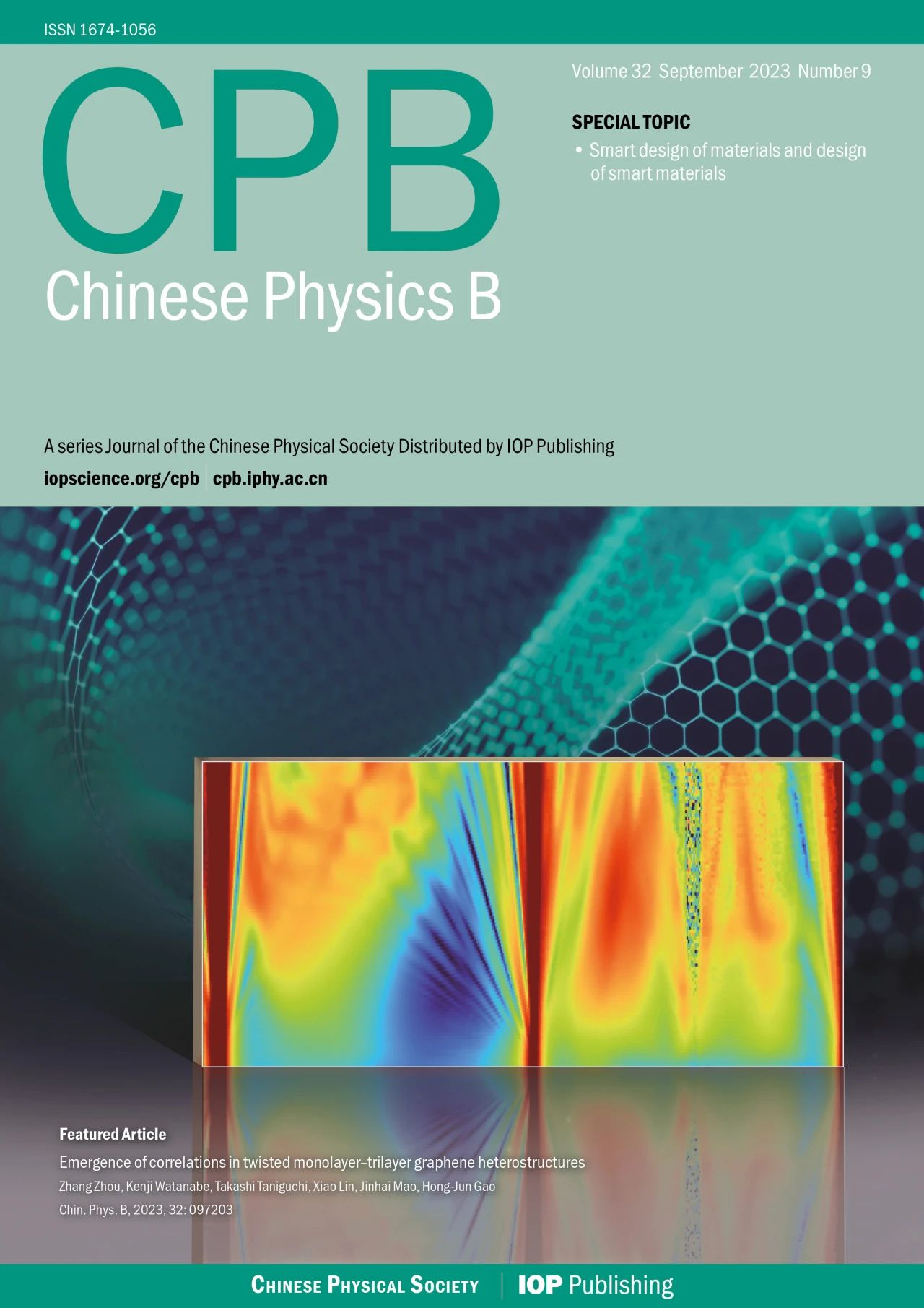



https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-3377544-1408049.html
上一篇:[转载]CPB2023年第8期编辑推荐文章
下一篇:[转载]CPB2023年第9期编辑推荐文章