https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.3c06878
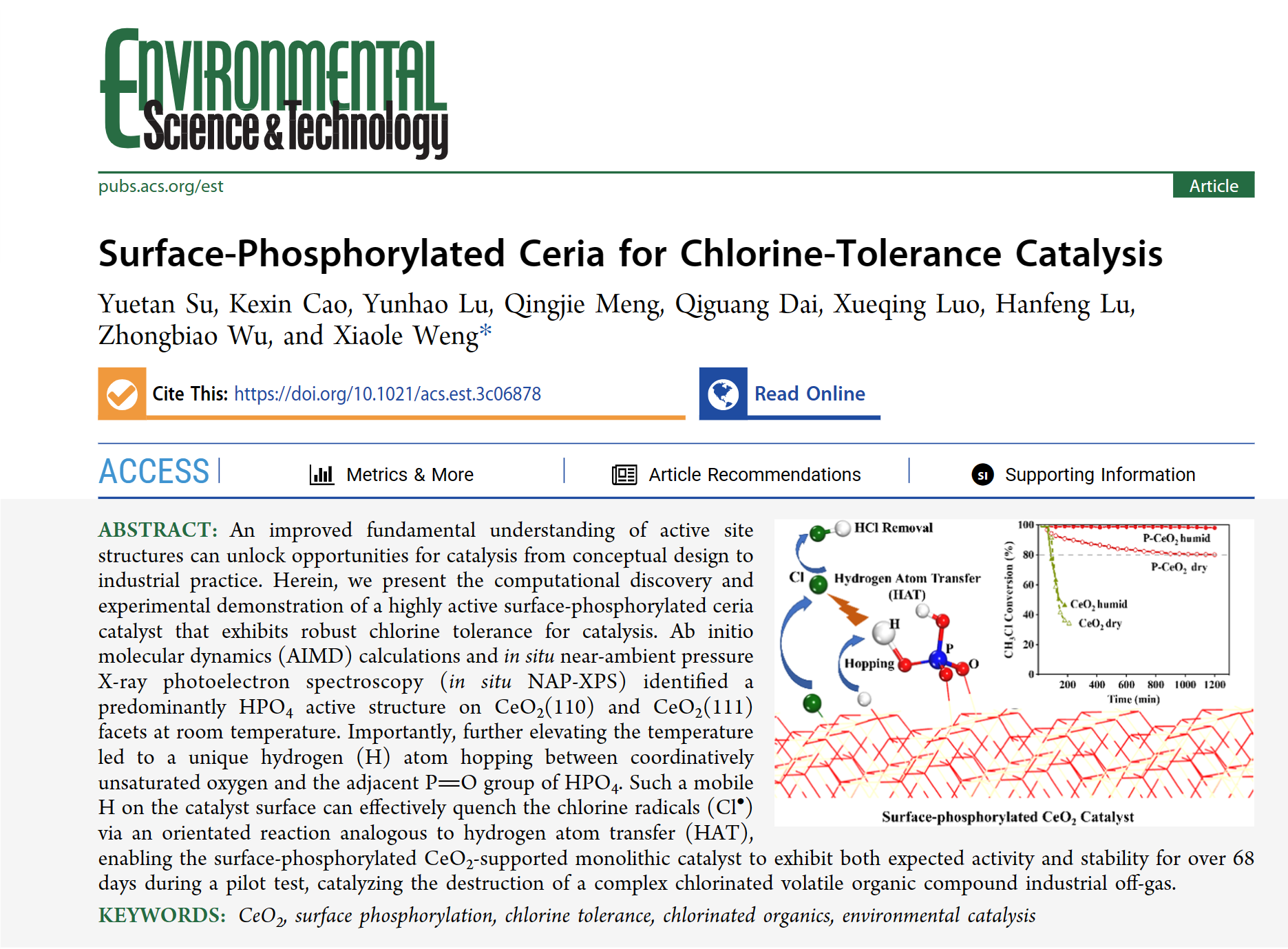
An improved fundamental understanding of active site structures can unlock opportunities for catalysis from conceptual design to industrial practice. Herein, we present the computational discovery and experimental demonstration of a highly active surface-phosphorylated ceria catalyst that exhibits robust chlorine tolerance for catalysis. Ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) calculations and in situ near-ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (in situ NAP-XPS) identified a predominantly HPO4 active structure on CeO2(110) and CeO2(111) facets at room temperature. Importantly, further elevating the temperature led to a unique hydrogen (H) atom hopping between coordinatively unsaturated oxygen and the adjacent P═O group of HPO4. Such a mobile H on the catalyst surface can effectively quench the chlorine radicals (Cl•) via an orientated reaction analogous to hydrogen atom transfer (HAT), enabling the surface-phosphorylated CeO2-supported monolithic catalyst to exhibit both expected activity and stability for over 68 days during a pilot test, catalyzing the destruction of a complex chlorinated volatile organic compound industrial off-gas.
有幸参与,很早之前发现H Hopping在氧化铈用于CVOCs催化燃烧时可能有所作用,翁教授做了全面的考察!
转载本文请联系原作者获取授权,同时请注明本文来自戴启广科学网博客。
链接地址:https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-3913-1412698.html?mobile=1
收藏


