博文
2023年3月嘲风作品集(二)
||

▲ Vol 57 Issue 09 | 07 March, 2023
Single-Atom Fe-N4 Sites for Catalytic Ozonation to Selectively Induce a Nonradical Pathway toward Wastewater Purification
Tengfei Ren, Mengxi Yin, Shuning Chen, Changpei Ouyang, Xia Huang, and Xiaoyuan Zhang
Nonradical oxidation has been determined to be a promising pathway for the degradation of organic pollutants in heterogeneous catalytic ozonation (HCO). However, the bottlenecks are the rational design of catalysts to selectively induce nonradicals and the interpretation of detailed nonradical generation mechanisms. Herein, we propose a new HCO process based on single-atom iron catalysts, in which Fe-N4 sites anchored on the carbon skeleton exhibited outstanding catalytic ozonation activity and stability for the degradation of oxalic acid (OA) and p-hydroxybenzoic acid (pHBA) as well as the advanced treatment of a landfill leachate secondary effluent. Unlike traditional radical oxidation, nonradical pathways based on surface-adsorbed atomic oxygen (*Oad) and singlet oxygen (1O2) were identified. A substrate-dependent behavior was also observed. OA was adsorbed on the catalyst surface and mainly degraded by *Oad, while pHBA was mostly removed by O3 and 1O2 in the bulk solution. Density functional theory calculations and molecular dynamics simulations revealed that one terminal oxygen atom of ozone preferred bonding with the central iron atom of Fe-N4, subsequently inducing the cleavage of the O–O bond near the catalyst surface to produce *Oad and 1O2. These findings highlight the structural design of an ozone catalyst and an atomic-level understanding of the nonradical HCO process.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.est.2c07653

▲ Vol 12 Issue 07 | 13 March, 2023
Flexible Skin Patch Enabled Tumor Hybrid Thermophysical Therapy and Adaptive Antitumor Immune Response
Xuyang Sun, Tao Wu, Minghui Duan, Bo Yuan, Xiyu Zhu, Hongzhang Wang, Jing Liu
Flexible Skin Patches
In article 2202872 by Xuyang Sun, Hongzhang Wang, Jing Liu and co-workers, a flexible skin patch with improved adhesiveness to skin is designed for conformable and non-invasive tumor therapy. This multifunctional technology can achieve severe destruction on tumor via an “ice and fire” mechanism, mediated by cryoablation, magnetic hyperthermia, as well as immune response activation.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adhm.202370034
▲ Vol 06 Issue 02 | 15 March, 2023
All-Climate Stretchable Dendrite-Free Zn-Ion Hybrid Supercapacitors Enabled by Hydrogel Electrolyte Engineering
Yuqi Jiang, Kun Ma, Meiling Sun, Yuanyuan Li, Jinping Liu
Hybrid supercapacitors have shown great potentials to fulfill the demand of future diverse applications such as electric vehicles and portable/wearable electronics. In particular, aqueous zinc-ion hybrid supercapacitors (ZHSCs) have gained much attention due to their low-cost, high energy density, and environmental friendliness. Nevertheless, typical ZHSCs use Zn metal anode and normal liquid electrolyte, causing the dendrite issue, restricted working temperature, and inferior device flexibility. Herein, a novel flexible Zn-ion hybrid supercapacitor (FZHSC) is developed by using activated carbon (AC) anode, δ-MnO2 cathode, and innovative PVA-based gel electrolyte. In this design, heavy Zn anode and its dendrite issue are avoided and layered cathode with large interlayer spacing is employed. In addition, flexible electrodes are prepared and integrated with an anti-freezing, stretchable, and compressible hydrogel electrolyte, which is attained by simultaneously using glycerol additive and freezing/thawing technique to regulate the hydrogen bond and microstructure. The resulting FZHSC exhibits good rate capability, high energy density (47.86 Wh kg−1; 3.94 mWh cm−3), high power density (5.81 kW kg−1; 480 mW cm−3), and excellent cycling stability (~91% capacity retention after 30 000 cycles). Furthermore, our FZHSC demonstrates outstanding flexibility with capacitance almost unchanged even after various continuous shape deformations. The hydrogel electrolyte still maintains high ionic conductivity at ultralow temperatures (≤−30°C), enabling the FZHSC cycled well, and powering electronic timer robustly within an all-climate temperature range of −30~80°C. This work highlights that the promising Zn metal-free aqueous ZHSCs can be designed with great multifunctionality for more practical application scenarios.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/eem2.12357
▲ Vol 11 Issue 11 | 21 March, 2023
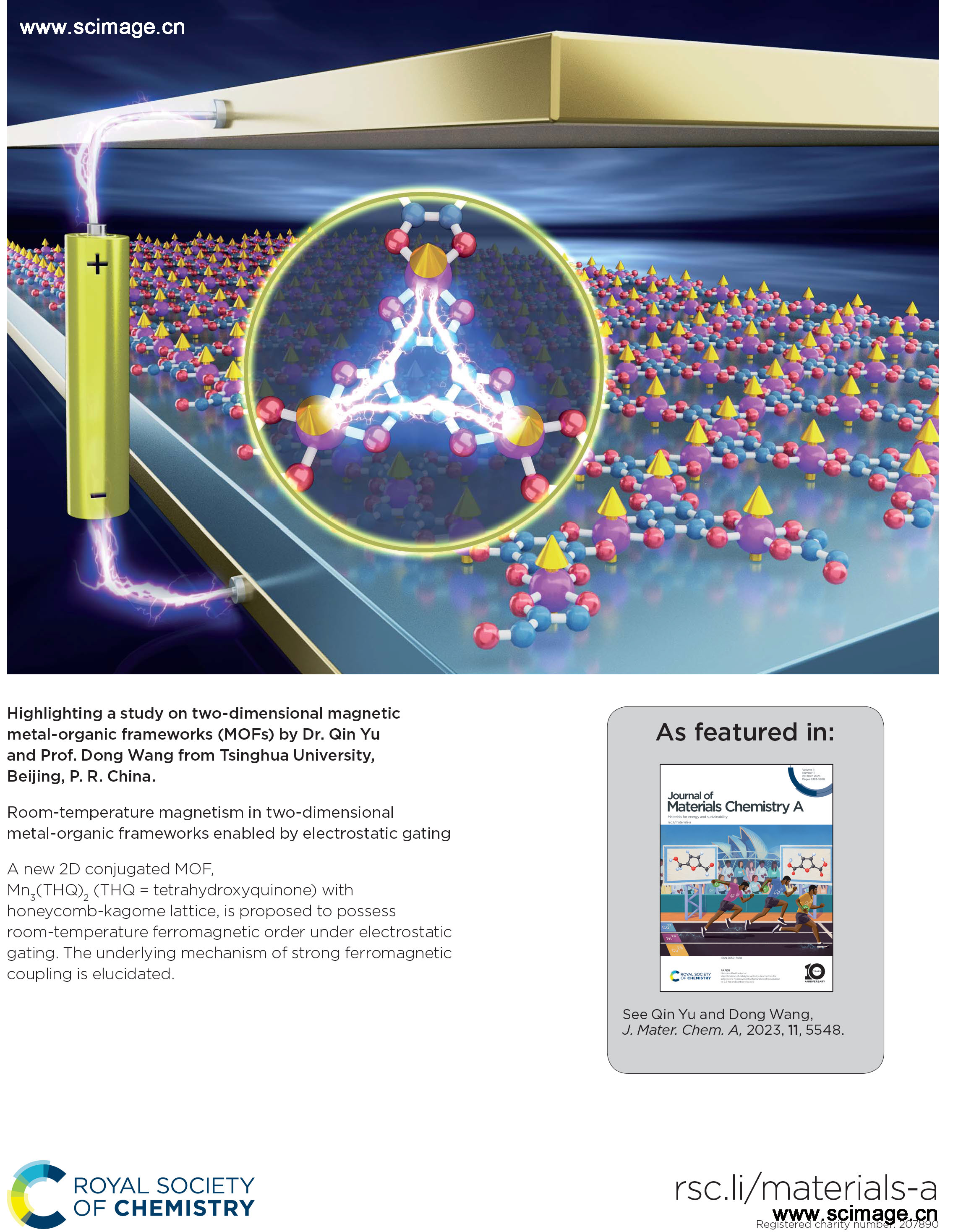
Room-temperature magnetism in two-dimensional metal–organic frameworks enabled by electrostatic gating
Qin Yu and Dong Wang
Two-dimensional (2D) magnetism has attracted intense attention in the area of low-dimensional materials and devices, with intriguing physics emerging and significant potential for applications in energy-efficient data storage and quantum computing. Although a robust magnetic order sustainable under room temperature is the most relevant issue for its practical applications, high temperature magnetism is rarely reported. 2D magnets obtained to date are often exfoliated from van der Waals atomic crystals with bulk magnetism. In this work, we propose a new type of 2D magnets, 2D conjugated metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), which are constructed by magnetic metal ions and conjugated ligands on a honeycomb-kagome lattice. By combining chemical modifications and an electrostatic gating approach, we attain a MOF, Mn3(THQ)2 (THQ = tetrahydroxyquinone) possessing the square-planar Mn–O coordination and minimal-sized ligand, which exhibits an ultra-high Curie temperature of 250 K in the neutral monolayer and 300 K in the hole doped one. These findings manifest both chemical and electrical means as powerful tools to tailor the magnetism of 2D MOFs on demand, and further highlights their prospect for applications in ultracompact spintronic devices.
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2023/ta/d2ta08540b
<静远嘲风动漫传媒科技中心>设计制作

购书链接:
☆科学的颜值:学术期刊封面故事及图像设计
https://item.jd.com/12802188.html
☆科技绘图/科研论文图/论文配图设计与创作自学手册:CorelDRAW篇
https://item.jd.com/13504674.html
☆科技绘图/科研论文图/论文配图设计与创作自学手册:Maya+PSP篇
https://item.jd.com/13504686.html
☆科技绘图/科研论文图/论文配图设计与创作自学手册:科研动画篇
https://item.jd.com/13048467.html#crumb-wrap
☆SCI图像语法-科技论文配图设计使用技巧
https://item.jd.com/10073529532924.html?bbtf=1


静远嘲风(MY Scimage) 成立于2007年,嘲风取自中国传统文化中龙生九子,子子不同的传说,嘲风为守护屋脊之瑞兽,喜登高望远;静远取自成语“宁静致远”,登高莫忘初心,远观而不可务远。



https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-519111-1389069.html
上一篇:2023年3月嘲风作品集(一)
下一篇:2023年3月嘲风作品集(三)