博文
Phenomics |基于高通量表型测量和机器学习的植物胁迫表型测量综述
|
《表型组学》(Phenomics)在线发表了华盛顿州立大学Karansher S. Sandhu、田纳西州立大学Jason P. de Koff等团队合作的题为A Comprehensive Review of High Throughput Phenotyping and Machine Learning for Plant Stress Phenotyping的综述。
论文DOI链接:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-022-00048-z
论文PDF链接:
https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s43657-022-00048-z.pdf
世界人口预计在2050年将达到约90亿至100亿,为满足急剧增长的人口需求,世界粮食生产需比现有水平提高约25-70%。然而,各种生物和非生物因素对植物作物造成的不利环境条件或压力,将导致其产量大幅下降,危及全球粮食安全。
植物表型测量被定义为对植物复杂性状的综合评估,如发育、生长、抗性、耐性、生理、结构、产量、生态,以及对评估这些复杂性状的单个定量参数的基本测量。传统的表型测量成本昂贵、费力、具有破坏性,并可能降低结果的显著性或精确性。在过去的十年中,具有多个传感器的地面和空中平台被迅速采用,用于在作物植物的整个发育阶段对各种生物和非生物胁迫进行表型测量(图1)。高通量表型测量(HTP)系统应用这些工具为非破坏性和有效的田间植物表型测量提供了巨大的潜力,它配备有单个或多个传感器的手动、半自动或自动平台,记录相关时间和空间数据,从而产生大量数据以供存储和分析。然而,这些高通量表型测量技术的使用所产生数据的体量之大,阻碍了从中进行推论的策略。机器学习和深度学习使用概率、统计、分类、回归、决策理论、数据可视化和神经网络等,将提取的信息与获取的表型联系起来。
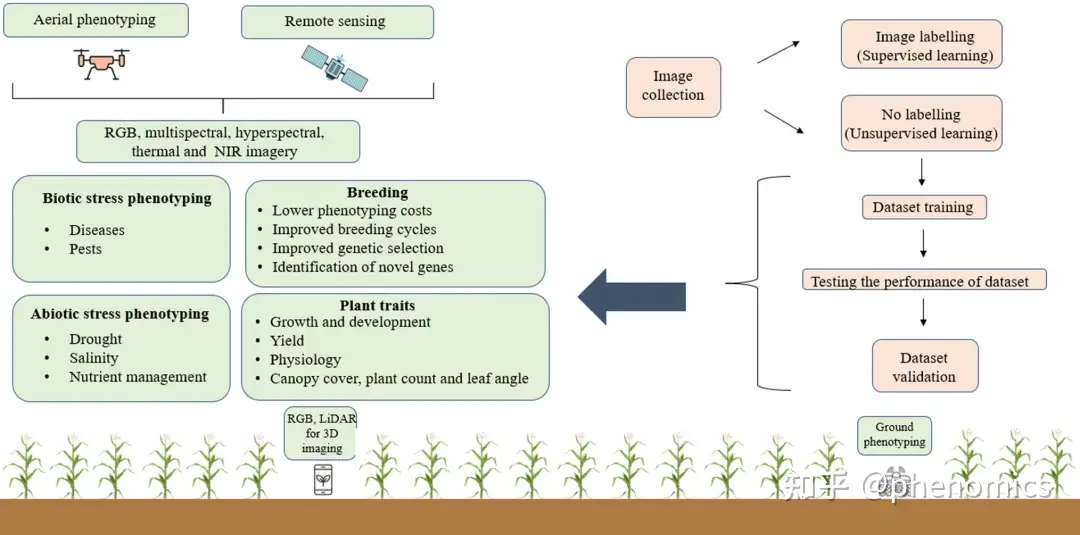
图1 用于田间植物胁迫检测的不同表型测量工具和平台
传统的机器学习方法需要利用计算和图像分析的专业知识,并耗费大量的精力来设计特征,这阻碍了其在性状表型上的应用。深度学习已经成为一种潜在的机器学习方法,它结合了先进的计算能力和海量数据集的优势,并允许分层数据学习。重要的深度学习模型包括多层感知器(Multilayer Perceptron, MLP)、生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Networks , GAN)、卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network , CNN)和循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network, RNN)(图2)。
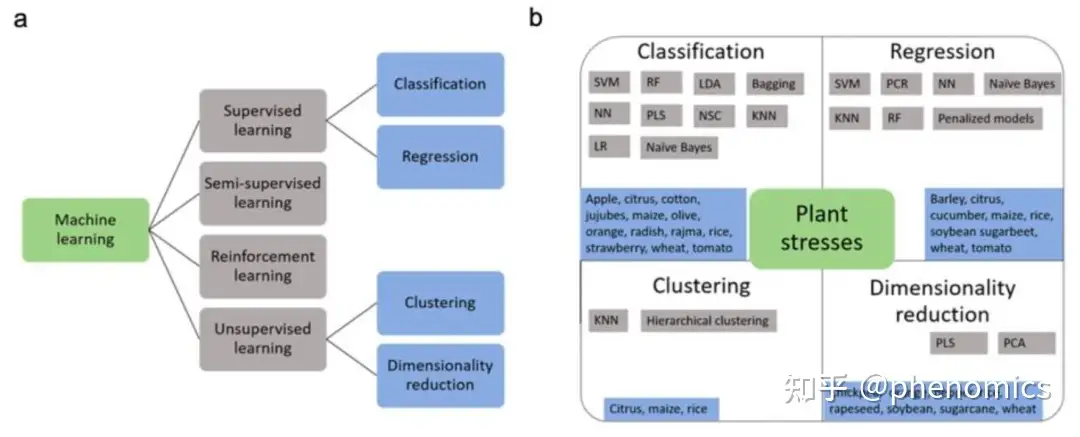
图2 用于高通量表型测量的机器学习和深度学习模型分类
总的来说,该综述为研究各种高通量表型测量平台提供了新思路,强调了机器学习和深度学习工具的应用,提出了当前面临的概念性挑战并对相关问题管理的未来前景提出了见解。
Abstract
During the last decade, there has been rapid adoption of ground and aerial platforms with multiple sensors for phenotyping various biotic and abiotic stresses throughout the developmental stages of the crop plant. High throughput phenotyping (HTP) involves the application of these tools to phenotype the plants and can vary from ground-based imaging to aerial phenotyping to remote sensing. Adoption of these HTP tools has tried to reduce the phenotyping bottleneck in breeding programs and help to increase the pace of genetic gain. More specifically, several root phenotyping tools are discussed to study the plant’s hidden half and an area long neglected. However, the use of these HTP technologies produces big data sets that impede the inference from those datasets. Machine learning and deep learning provide an alternative opportunity for the extraction of useful information for making conclusions. These are interdisciplinary approaches for data analysis using probability, statistics, classification, regression, decision theory, data visualization, and neural networks to relate information extracted with the phenotypes obtained. These techniques use feature extraction, identification, classification, and prediction criteria to identify pertinent data for use in plant breeding and pathology activities. This review focuses on the recent findings where machine learning and deep learning approaches have been used for plant stress phenotyping with data being collected using various HTP platforms. We have provided a comprehensive overview of different machine learning and deep learning tools available with their potential advantages and pitfalls. Overall, this review provides an avenue for studying various HTP platforms with particular emphasis on using the machine learning and deep learning tools for drawing legitimate conclusions. Finally, we propose the conceptual challenges being faced and provide insights on future perspectives for managing those issues.
作者简介
通讯作者:Karansher Sandhu

Karansher Sandhu 博士,华盛顿州立大学。主要研究方向为植物育种和遗传学,致力于结合基因组学、表型学和数据科学技能来提高大豆的遗传增益和产品开发。
通讯作者:Jason de Koff

Jason de Koff 博士,田纳西州立大学。主要研究方向为与生物能源、作物生产和土壤科学相关的研究等。
Phenomics期刊简介

Phenomics是一本新创的同行评审国际期刊,聚焦表型组学前沿研究,搭建全球表型组学领域专家交流的国际平台,推动该领域相关的理论创新和学科发展。
本期刊拥有强大的国际编委团队,复旦大学金力院士担任主编,美国系统生物学研究所Leroy Hood院士、澳大利亚莫道克大学Jeremy Nicholson院士、德国莱布尼兹环境医学研究所Jean Krutmann院士、复旦大学唐惠儒教授共同担任副主编,复旦大学丁琛教授担任执行主编,另有来自全球多国的三十多位著名科学家共同组成编委团队,以及四十多位青年科学家组成青年编委团队。
我们诚挚地邀请广大科研人员投稿!
Phenomics官网:https://www.springer.com/journal/43657
投稿链接:https://www.editorialmanager.com/pnmc/
编辑部邮箱:phenomics@ihup.org.cn、phenomics@fudan.edu.cn
欢迎关注Phenomics官方公众号

文章来源:人类表型组计划公众号
https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-3558836-1388369.html
上一篇:Phenomics| 深度学习模型助力掌纹表型特征提取和分类
下一篇:Phenomics| 使用机器学习方法研究哥斯达黎加在接种疫苗前诊断SARS-CoV-2感染的临床情况