博文
写在开学第一天—气候变化未来的趋势
||
今年开学比往常似乎要晚一些,经过一个多月的休整,现在有回到我们美丽的校园(希望正在施工建筑,快快修好,这样就会更加美丽了)。
开学第一天,似乎论文是关键(现在师弟、师妹们都在忙碌着,整理数据,学习新的数学方法),但是我认为,地图是我们地理学的“第二语言”(第一语言我想是就是我们的文字吧,貌似说成第一语言也是可以的),一点要会熟练地应用它,这样文章才有地理特色!
我们的研究方向:全球气候变化与区域灾害防治。最近的频繁暴雪和寒潮来袭,使得我们的研究方向一下成为了热点问题,全球科学家总动员,集体关注气候未来变化趋势,到底是变暖,还是变冷,真是有趣的话题,有兴趣的可以看一下,最近我们《资源科学》关于气候变化的文章,我们的观点也很有意思!
现将中、英文摘要摘录下来:
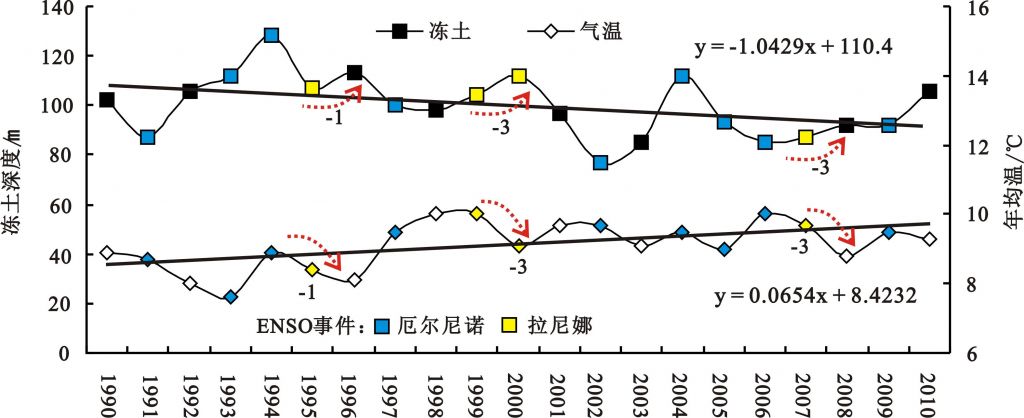
摘 要:选取陕北沙漠化逆转区榆林作为研究对象,采用气候倾向率、Mann-Kendall非参数检验和小波分析法等气候诊断方法,探讨了1971-2010年榆林地区气温时空分布规律、变化趋势及其影响因素。结果表明:榆林南北两大地貌单元气温逐年升高,北部增温幅度大于南部,气候倾向率关系为:陕南<关中<全国<南部丘陵沟壑区<北部风沙草滩区;南部丘陵沟壑区气温突变(1989年)早于北部风沙草滩区(1994年)。气温增加幅度存在差异,空间格局呈现“冷快暖慢,整体一致增加”的变化特征。榆林地区气温变化完全符合全球变化规律,其驱动力是自然因素和人类活动共同作用的结果,太阳辐射由强到弱,加之La Nina 事件频发,在一定程度上减缓了人类活动带来的增温。
Abstract: The “Three North Shelterbelt Program” and “Grain-for-Green Project” carried out by the governments were the dominant contributors to the desertification severity reversal in north china. Climate change and human activities were somewhat responsible for the decrease in desertification severity but significantly affected the increase in desertification extent. In order to clarifying the causes of rehabilitation in an agro-pastoral transitional zone of northern Shaanxi, this paper, based on the meteorological data of the 12 stations(1971-2010) in Yulin region, analysis the fundamental characteristics, temporal-spatial distribution and reasons of temperature change in the desertification reversal region, using methods of linear regression, Mann-Kendall mutation test, analysis of wavelets, kriging interpolation and other Climate diagnosis method. Research shows that the trend is concurrent that become warmer over the several decades, the increment of temperature in the northern region of Yulin had larger than that in the southern region; in recent 10 years temperature becomes cold in two areas. Both extreme high and average temperature declined gradually since 2000. The order of climate of temperature is that the south of Qinling mountains(0.121℃/10a)<Guangzhong(0.203℃/10a)<other regions of china (0.26±0.032℃/10a)<the south area(0.291℃/10a)<the north area(0.437℃/10a). The temperature mutation of south (1989) is earlier than the north (1994), which is earlier than the other regions of china (1993). The temperature is changing; however, the spatial distribution is largely unchanged, that is the characterized with a decrease from the southeast to northwest. The trends of temperature variation have certain spatial discrepancy. The geographic centers of temperature warming in the study area have moved to the southwest (Dingbian, jingbian). Based the climate characteristics, it was found that the influence of climate changing mainly reflects nature and human actives. Observations of temperatures in Yuyang or so support the hypothesis of the anthropogenic impact, but natural factors such as solar activity, El Nino/La Nina events, atmospheric circulation and the decreasing of relative humidity also take part in the modulation of temperature changes, especially in frequency band of inter-decadal variability. Atmospheric radiation is dropping year by year, La Nina frequently occurred, thus resulting in temperature cooling, which weaken the impact of human actives. A linear trend of sunshine duration during 1990–2010 is about -498.6h/ decade. Moreover, a linear trend of relative humidity during 1990–2010 is about -3.26%/ decade. There is pervasive evidence for nature and human actives forcing of the climate, however, its influencing mechanism is remained to be further investigated.
结论:日照时数逐年下降(外来的热量减少),相对湿度亦在下降,空气中的水分减少,加之ENSO事件频发,在一定程度上,对气温的上升有减缓作用。尽管近20年气温上升速度有所下降(这一点在区域冻土的变化也有反应),但是增加趋势没有改变!

https://m.sciencenet.cn/blog-682518-536992.html
下一篇:地理学的六本好书